Jim Roberts, director of technical services for the university’s athletic department, described this as a happy coincidence as opposed to a larger strategy to bring sports technology to the Badger faithful. “Knowing that the new Wi-Fi system was coming, the group working on the app upgrade was able to incorporate more features, knowing fans could take advantage of the improved Wi-Fi and not rely solely on cellular data plans,” Roberts said.
Editor’s note: This profile is an excerpt from our latest STADIUM TECHNOLOGY REPORT, which is available for FREE DOWNLOAD from our site. In addition to this stadium tech deployment profiles we also take an in-depth look at the new trend of deploying Wi-Fi and DAS antennas under seats, and provide a wireless recap from Super Bowl 50. GET YOUR COPY today!
The Wisconsin venues are Camp Randall, a bowl-style football stadium with a capacity of 80,321; and nearby Kohl Center, used for hockey, basketball, concerts and other live events with room for 17,230. The LeBahn Arena, built for women’s ice hockey with a capacity of 2,273, is also included. In part because of their proximity, Roberts and his team used the upgrades to replace and enhance the underlying infrastructure for the venues – core switching, Wi-Fi access points, an IPTV system, cabling, electrical power and HVAC improvements — $11 million for the whole package, according to Roberts.
“Due to the expected size of the population connecting to Wi-Fi, we had to upgrade the entire network,” he explained, adding that the previous 10/100 Mbps backbone with Gigabit Ethernet uplinks and its 32,000 MAC address capacity was insufficient for the job.
“We upgraded our core to some pretty big Cisco routers at each venue that could handle 128,000 MAC addresses, with 10-gigabit fiber to all 33 telecom rooms within the Camp Randall complex,” he said; they also added about 1,100 wireless APs. Camp Randall got upgraded during the summer of 2014; the Kohl Center and LeBahn were done a year later.
Camp Randall proved to be the largest test, both from an engineering and design perspective. Built in 1917, its open bowl lacks the overhangs from which RF engineers love to hang antennas and other infrastructure.“The east side of the bowl became our biggest challenge with getting the signal to penetrate deep enough into the sections,” Roberts said, adding that the problem was especially acute for seats closest to the field, where the first few rows are tarped over. Initially, APs were installed below the tarps, but the signal only carried 10 rows back.
“We ended up mounting the APs on the front, 4-6 feet up from ground level,” and above the tarps, he explained. “They don’t affect the sight lines for spectators. But getting the APs to shoulder height from waist height definitely helped us get it back to row 25.”
APs were also mounted just above the entry tunnels, where the hardware and antenna could be attached to railings and concrete. Cisco is the University of Wisconsin’s AP vendor; the deployment uses Cisco model 3700s.
Roberts and his team also ran into some structural issues with waterproofing and cabling that kept them from putting in more APs in the student section. They had to re-calculate where the APs would go; consequently, coverage can be spotty in the student section, which is exacerbated by the high density of phones in that part of the stadium. AT&T and Verizon both have DAS infrastructure in Camp Randall that helps coverage, but Roberts and his team are looking at long-term solutions for Wi-Fi coverage in that section and throughout Camp Randall.The University of Wisconsin worked closely with AmpThink on a facility-wide Wi-Fi analysis, according to Bob Lahey, a network engineer in the athletic department. AmpThink did the design and tuning and worked out some issues in advance. “Our facilities staff and [AmpThink] discussed locations for best coverage and worked through the aesthetics before we started the project,” Lahey said. AmpThink was also onsite during the first year to see how the Wi-Fi performed with people in the bowl. “You can only figure out so much without people there,” Lahey laughed.
Getting Online at Camp Randall
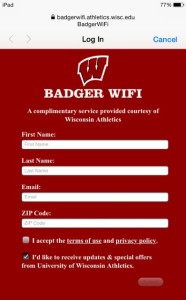
The stadium’s fan-facing wireless network, Badger WiFi, is a captive portal that asks users for their name, email address and zip code. There are also two boxes: one, users must check to agree to terms and conditions of service; the second allows the university to send them emails, and by default, the second box is checked. “Our plan is to send them email surveys and allow them to remain on the system and not have to re-authenticate every time they come to one of our buildings,” Lahey said. “But if they uncheck, they have to re-authenticate.”
The university does no bandwidth limiting or throttling back usage once users are logged in. “We’ve got dual 10-gigabit links and 100-gigabit to the world, so we’re not too concerned about overall bandwidth,” Lahey said. “We limit each radio in the AP to a maximum of 200 clients. It doesn’t happen often, but we see it occasionally.” Camp Randall users normally get at least 1 Mbps bandwidth — plenty for checking scores or posting to social media, Lahey added. Kohl Center users average 40-60 Mbps because the venue is less dense.
At present, 65-70 percent of Badger Wi-Fi clients are on 5 GHz spectrum rather than 2.4 GHz. Roberts finds the 5 GHz band easier to manage, and said users get a better experience. “If we have problems with wireless, it is most times an older couple with their iPhone 4,” Roberts said. “APs can only do so much, but sometimes a phone [using 2.4 GHz spectrum] will want to connect with an AP a half mile across the field rather than one that’s 10 feet away.”He also said the maximum number of unique clients for Camp Randall is about 26,000, or 37 percent of the crowd. “We assume that’s going to keep growing and we’ll have to augment the system,” he said. “At some point we won’t have enough access points.”
Game Day Gets a Badger Refresh
Concurrently, the Badger Game Day smartphone app was getting new features like live video replay and interaction with Bluetooth-based beacon technology. The app’s first iteration was initially for football, then expanded to all 10 sports that sell tickets; the latest version embraces all 23 sports at the University of Wisconsin, men’s and women’s. “Not many schools have all their sports represented, so while the traffic may not be high on rowing, it’s a great recruitment tool,” said Ben Fraser, director of external engagement for the athletics department. “So it helps there with the coaches sending out links or for parents and other supporters.”
It also helps with fans. “Collegiate and professional sports venues are looking for how to keep fans entertained and also allow them to participate in the game via social media and other methods,” noted Tam Flarup, director of the athletic department’s website services. When there’s break in the action, Badger fans are busy posting to Facebook, Instagram and of course, Wisconsin’s infamous Jump Around. “Twitter’s also allowing Periscope live video in its tweets now,” Flarup added. “Our fans will like that – it keeps them in the stands with a great game day atmosphere and experience.”
The university developed the first two iterations of Badger Game Day internally but chose to outsource the upgrade to sports-app developer YinzCam in June 2015 and gave them a tight deadline to meet — Aug. 30, just in time for Badger football season. YinzCam delivered on time, and then met an Oct. 15 deadline for revisions and tweaks, Fraser said.
Badger Game Day now includes live video replay from four different camera angles; YinzCam’s secret sauce makes streaming video across Wi-Fi more efficient. “Video would have been impossible without the Wi-Fi investment we made,” Fraser said.
Unlike previous iterations that only allowed the participation of a single sponsor, the new Badger Game Day app gives the university the ability to sell individual pages and sports, Fraser said.
Perhaps the leading edge of Badger Game Day is its use of Bluetooth-based beacon technology and messaging with geo-fencing. Gimbal Inc. worked with the university customize the technology; Fraser and his team did some social media messaging to alert fans to the feature and to remind them to turn it on.The first remote use of messaging with beacons and geo-fencing was in Dallas for Wisconsin’s season opener in Dallas at AT&T Stadium; the feature was then used continually at both Camp Randall and the Kohl Center.
“We continued to use this messaging on the road for the Holiday Bowl in San Diego,” Fraser said. “Messages varied from welcome messages that were linked to videos from our players, to informational messages that informed fans about events, to scavenger hunts that engaged our fans at these sites.”
When users first download the app, there’s a proximity allowance message that they must activate to receive beacon messages. So far, the university has sent out 46 unique messages, 21 of which were geo-fenced. At each home game, they geo-fence Camp Randall with a welcome video from players; they reached an average number of 1,160 fans per game with these welcome messages and videos.
“We’re still learning how fans are using [beacons and Bluetooth], and we’re trying not to hit them with too many ads,” Fraser said. By building their trust, it encourages fans to leave their Bluetooth on for the signal to find them. “And we are looking for ways to improve it,” he added. Potential future additions: Features that show the length of lines at concession stands and restrooms, and an online lost and found. They’re also looking for more robust scheduling information inside the app — such as which broadcast network is carrying the game, along with links to Wisconsin’s video stream and live stats.
App development and a new server cost the university about $100,000, according to Fraser and Flarup. Since August 2015, there have been 123,000 downloads of Badger Game Day and nearly 1 million page views. Average time spent per game on the audio feature of the app is about 14 minutes. There’s more room to grow as fans continue to download and use the app; there’s plenty of revenue upside as well as sponsors discover multiple avenues for their messaging and content.