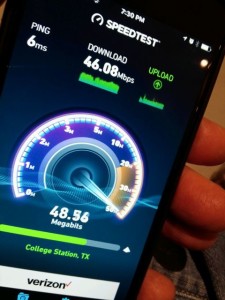
One of the many maxed-out speed tests we took at Texas A&M’s Kyle Field. All photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any photo for a larger image)
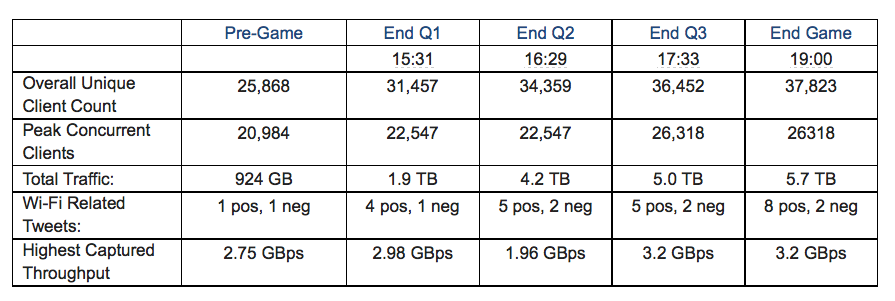
In fact, after reviewing loads of live network-performance data of Kyle Field’s new Wi-Fi and DAS in action, and after maxing out the top levels on our speed tests time after time during an informal walk-around on a game day, we’ve come to the conclusion that Kyle Field has itself a Spinal Tap of a wireless deployment. Meaning, that if other stadium networks stop at 10, this one goes to 11.
Movie references aside, quite simply, by the numbers Kyle Field’s wireless network performance is unequaled by any other large public venue’s we’ve tested in terms of raw speed and the ability to deliver bandwidth. With DAS and Wi-Fi speed measurements ranging between 40 Mbps and 60+ Mbps pretty much everywhere we roamed inside the 102,512-seat venue, it’s a safe bet to say that the school’s desire to “build the best network” in a stadium hit its goal as best as it could. And since the school spent “north of $20 million” on the network, perhaps it’s no surprise that it’s the fastest anywhere.
Our full profile of our in-depth visit to College Station to see this network in action can be found in our latest STADIUM TECH REPORT, our COLLEGE FOOTBALL ISSUE for 2015. You can download the report for free, right now! In addition to the Texas A&M profile you will find in-depth looks at wireless deployments at Kansas State, Ole Miss, Oklahoma and the venerable Rose Bowl — so download your copy today!
Audible to optical made the difference
Inside our latest 40+ page report you will get a full breakdown on how the Texas A&M network came to be — in an exclusive interview with Phillip Ray, Vice Chancellor for Business Affairs at The Texas A&M University System, you hear for the first time how much the Kyle Field network cost — “north of $20 million” — as well as how much the top two wireless carriers paid to be a part of it. Want to know? Then download the report!
And while the Kyle Field story is our lead article, that’s not all you’ll find in our latest in-depth exploration of stadium technology deployments. Reporter Terry Sweeney checks out the new DAS deployment blanketing Pasadena’s Rose Bowl, perhaps one of the toughest old-style stadium construction challenges to try to bring in wireless coverage. We also have profiles of Wi-Fi deployments at Kansas State and at Ole Miss, and a feature about covering RV parking lots with Wi-Fi at the University of Oklahoma. To top it all off we have some Wi-Fi cost/benefit analysis from yours truly, and a bonus photo feature by photographer Phil Harvey, who accompanied MSR for a recent visit to AT&T Stadium.
We’d like to take a quick moment to thank our sponsors, which for this issue include Mobilitie, Crown Castle, SOLiD, CommScope, Aruba (a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company), JMA Wireless, Corning, 5 Bars, Extreme Networks, and ExteNet Systems. Their generous sponsorship makes it possible for us to offer this content free of charge to our readers. We’d also like to thank you for your interest and continued support. Thanks for reading and enjoy the COLLEGE FOOTBALL ISSUE!