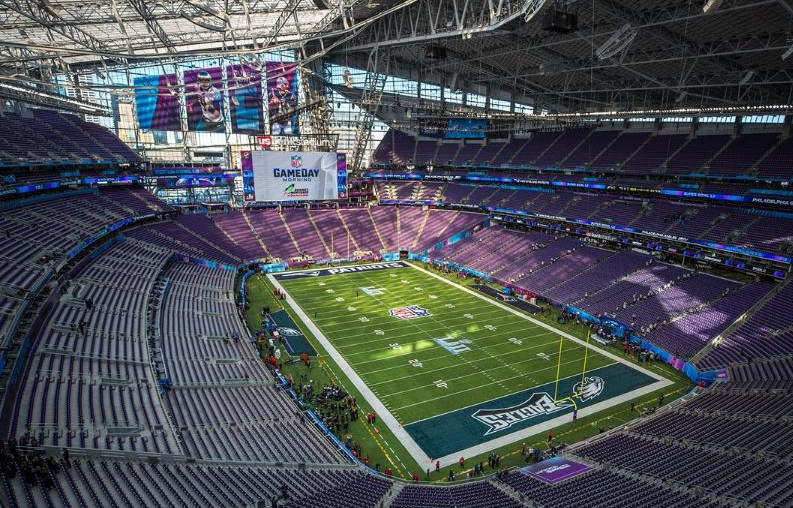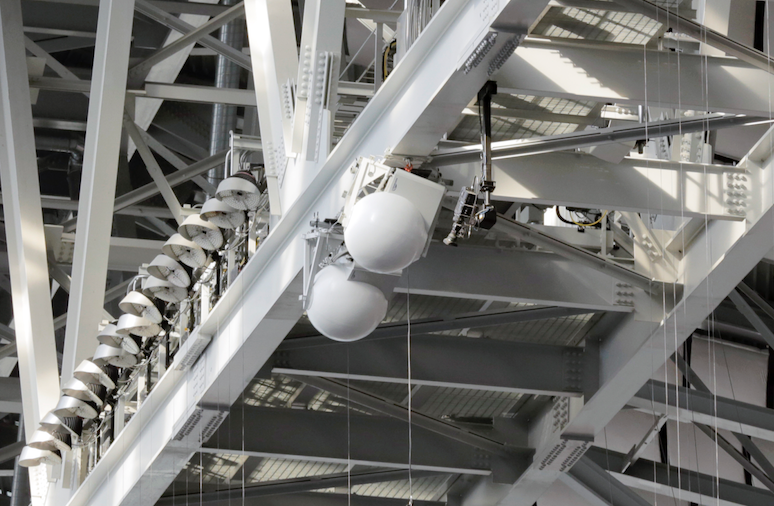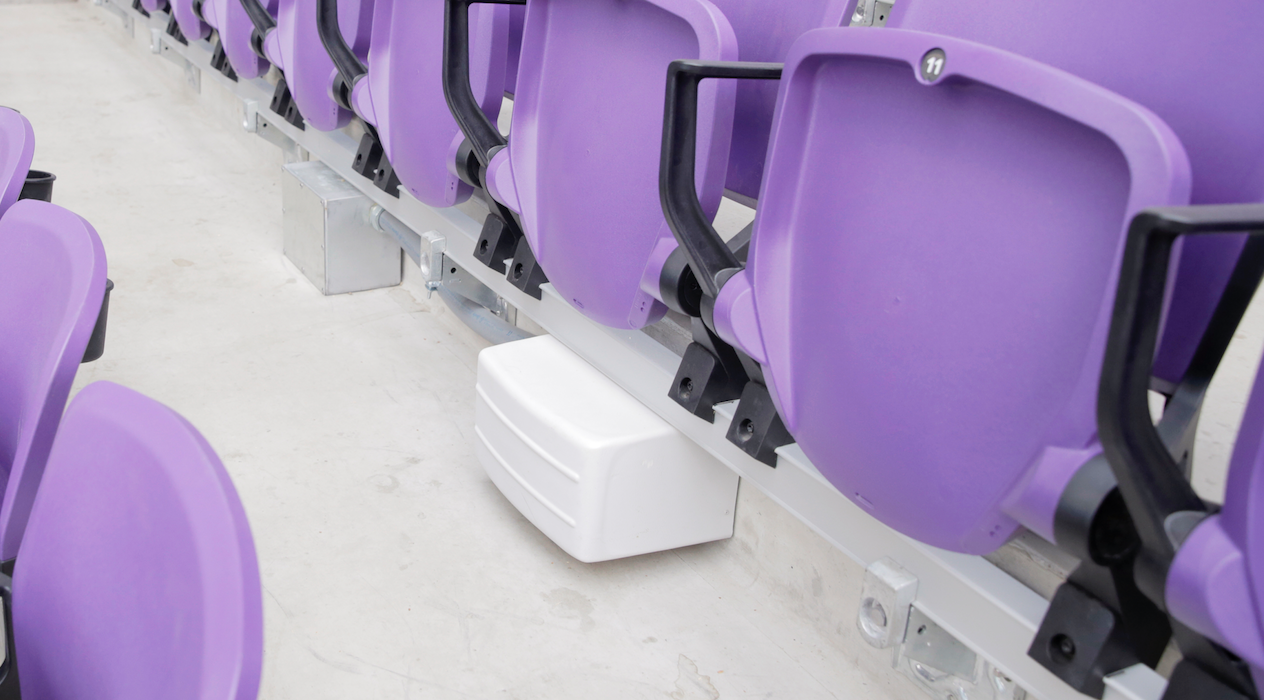
A Wi-Fi handrail enclosure at U.S. Bank Stadium in Minneapolis. Credit: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any photo for a larger image)
According to statistics compiled by Extreme Networks during the Philadelphia Eagles’ thrilling 41-33 victory over the New England Patriots Sunday night, the AmpThink-designed network which uses Cisco Wi-Fi gear also saw 40,033 unique users — 59 percent of the 67,612 in attendance — a new top percentage total for any single-game network experience we’ve been told about. (The Dallas Cowboys saw approximately 46,700 unique Wi-Fi users during a playoff game last season, about 50 percent of attendance at AT&T Stadium.)
The network also saw a peak concurrent connection of 25,670 users, and a peak data transfer rate of 7.867 Gbps, according to the numbers released by Extreme. Though Extreme gear was not used in the operation of the network, Extreme has a partnership deal with the NFL under which it provides the “official” network analytics reports from the Super Bowl.
The final total of 16.31 TB easily puts Super Bowl 52 ahead of the last two Super Bowls when it comes to Wi-Fi data use. Last year at NRG Stadium in Houston, there was 11.8 TB of Wi-Fi use recorded, and at Super Bowl 50 in 2016 there was 10.1 TB of Wi-Fi data used at Levi’s Stadium in Santa Clara, Calif. So in reverse chronological order, the last three Super Bowls are the top three Wi-Fi events, indicating that data demand growth at the NFL’s biggest game shows no sign of slowing down. Combined with the 50.2 TB of cellular data used in and around the stadium on game day, Super Bowl 52 saw a total of 66.51 TB of wireless traffic Sunday in Minneapolis.
Confetti fills the air inside U.S. Bank Stadium after the Philadelphia Eagles defeated the New England Patriots in Super Bowl LII. Credit: U.S. Bank Stadium
“AmpThink, CenturyLink and Cisco designed and built a world-class wireless system for U.S. Bank Stadium that handled record-setting traffic for Super Bowl LII,’ Kingsbury said. “AmpThink president Bill Anderson and his team of amazing engineers were a pleasure to work with and the experts at Cisco Sports and Entertainment supported us throughout the multi-year planning process required for an event of this magnitude. High-density wireless networking is such a challenging issue to manage, but I am very happy with our results and wish the team in Atlanta the best next year. The bar has been raised.”
THE LATEST TOP 10 FOR WI-FI
1. Super Bowl 52, U.S. Bank Stadium, Minneapolis, Minn., Feb. 4, 2018: Wi-Fi: 16.31 TB
2. Super Bowl 51, NRG Stadium, Houston, Feb. 5, 2017: Wi-Fi: 11.8 TB
3. Super Bowl 50, Levi’s Stadium, Santa Clara, Calif., Feb. 7, 2016: Wi-Fi: 10.1 TB
4. Minnesota Vikings vs. Philadelphia Eagles, NFC Championship Game, Lincoln Financial Field, Philadelphia, Pa., Jan. 21, 2018: Wi-Fi: 8.76 TB
5. Kansas City Chiefs vs. New England Patriots, Gillette Stadium, Foxborough, Mass., Sept. 7, 2017: Wi-Fi: 8.08 TB
6. Green Bay Packers vs. Dallas Cowboys, Divisional Playoffs, AT&T Stadium, Arlington, Texas, Jan. 15, 2017: Wi-Fi: 7.25 TB
7. Southern California vs. Notre Dame, Notre Dame Stadium, South Bend, Ind., Oct. 21, 2017: 7.0 TB
8. WrestleMania 32, AT&T Stadium, Arlington, Texas, April 3, 2016: Wi-Fi: 6.77 TB
9. Super Bowl 49, University of Phoenix Stadium, Glendale, Ariz., Feb. 1, 2015: Wi-Fi: 6.23 TB
10. Georgia vs. Notre Dame, Notre Dame Stadium, South Bend, Ind., Sept. 9, 2017: Wi-Fi: 6.2 TB
U.S. Bank Stadium in Minneapolis before the start of Super Bowl LII























