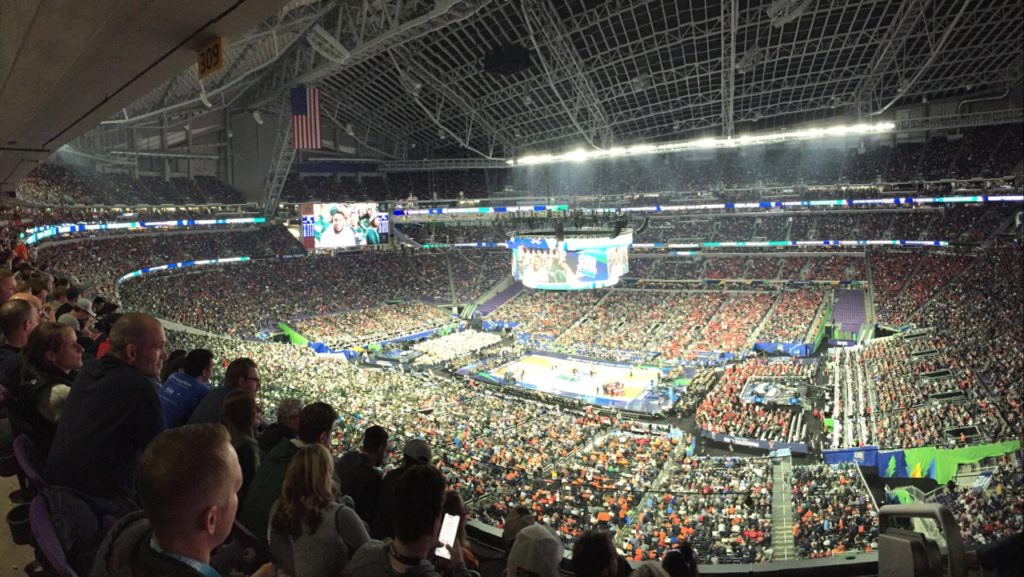
The standing section at Allianz Field for the opening game this spring. Credit: Minnesota United (click on any picture for a larger image)
The striking new $250 million facility, opened in April just off the highway that connects Minneapolis to St. Paul, is a looker from first sight, especially at night if the multi-colored lights in its cursive outside shell are lit. Inside, the clean sight lines and close-to-the-pitch seating that seems a hallmark of every new soccer-specific facility are accompanied by something that’s not as easy to detect: A solid fan-facing Wi-Fi network with approximately 480 Cisco access points, in a professional deployment that wouldn’t seem out of place at any larger facility, like an NFL stadium.
Actually, the Wi-Fi network inside Allianz Field is somewhat more conspicuous than many other deployments, mainly because instead of hiding or camouflaging the APs, most have very visible branding, letting visitors know that the Wi-Fi is “powered by” Atomic Data.
Who is Atomic Data? Though perhaps better known for their data center and enterprise business managed-services prowess, the 215-person Minneapolis-based firm also has a developing track record in stadium technology deployments, including a role as part of the IT support team for the launch of U.S. Bank Stadium two years ago. In what is undeniably a unique arrangement, Atomic Data paid for and owns the network infrastructure at Allianz Field, providing fan-facing Wi-Fi as well as back-of-house connectivity as a managed service to the team as well as to internal venue vendors like concessionaires.
LOCAL PARTNER EARNS TEAM’S TRUST
Editor’s note: This report is from our latest STADIUM TECH REPORT, an in-depth look at successful deployments of stadium technology. Included with this report is a profile of the new Wi-Fi network at Chesapeake Energy Arena in Oklahoma City, and an in-depth research report on the new Wi-Fi 6 standard! DOWNLOAD YOUR FREE COPY now!
While most new stadium builds often look for network and technology firms with a bigger name or longer history, Atomic Data was well known to the Minnesota team, having been a sponsor even before the club moved up to MLS.

One of the Cisco Wi-Fi APs installed by Atomic Data inside the new Allianz Field in Minneapolis. Credit: Paul Kapustka, MSR
“They [Atomic Data] are a very strong local company and we knew of their work, including at U.S. Bank Stadium,” Wright said. “Jim has also been a huge advocate of the [soccer] club, even before they moved to MLS. Their history is solid, and they [Atomic Data] have an incredible reputation.”
As the team prepared to move into its under-construction home, Wright said that originally having a high-definition wireless network wasn’t in the cards.
“The original plan was not to have a robust Wi-Fi network,” Wright said, citing overall budget concerns as part of the issue. But when he was brought in as CEO he was looking for a way to change the direction and have a more digital-focused fan experience – and he said by increasing Atomic Data’s partnership, the company and the team found a way to make it happen.
As described by both Wright and Atomic Data, the deal includes having Atomic Data pay for and own the Wi-Fi network components, and also to act as the complete IT outsourcer for the team, providing wired and wireless connectivity as a managed service.
“When you look at the demographic of our fans, they’re mostly millenials and we wanted to have robust connectivity to connect with them,” Wright said. “Over time we were able to negotiate a deal [with Atomic Data] to build what I think is the most capable Wi-Fi network ever for a soccer-specific venue. I think we’ve turned some heads.”
UNDER SEAT AND OUTSIDE THE DOORS
Just before the stadium hosted its first league game, Mobile Sports Report got a tour of the facility from Yagya Mahadevan, enterprise project manager for Atomic Data and sort of the live-in maestro for the network at Allianz Field. Mahadevan, who worked on the U.S. Bank Stadium network deployment before joining Atomic Data full-time, was clearly proud of the company’s deployment work, which fit in well with the sleek designs of the new facility.
For the 250 APs in the main seating bowl, Atomic Data used a good amount of under-seat AP deployments, since many of the seats have no overhang. A mix of overhead APs covers the seating areas that do have structures overhead, and more APs – which are clearly noticable, including some APs painted white to pop out against black walls and vice versa – are mounted along concourse walkways as well as on the outside of the main entry gates. Since MNUFC is a paperless ticketing facility, Mahadevan said Atomic Data paid special attention to entry gates to make sure fans could connect to Wi-Fi to access their digital tickets.Wright, who called Atomic Data’s devotion to service “second to none,” noted that before the first three games at the new stadium, Atomic Data had staff positioned in a ring around the outside of the field, making sure fans knew how to access their tickets via the team app and the Wi-Fi network.
“The lines to get in were really minimized, and that level of desire to deliver a high-end experience is just the way they think,” Wright said of Atomic Data.
According to Atomic Data the network is backed by two redundant 10-Gbps backbone pipes (from CenturyLink and Consolidated Communications) and is set up to also provide secure Wi-Fi connectivity to the wide number of independent retail and concession partners. Mahadevan also said that the network has a number of redundant cable drops already built in, in case more APs need to be added in the future. The stadium also has a cellular distributed antenna system (DAS) built by Mobilitie, but as of early this spring none of the carriers had yet been able to deploy gear.
Even the chilly temperatures at the team’s April 13 home opener didn’t keep fans from trying out the new network, as Atomic Data said it saw 85 gigabytes of Wi-Fi data used that day, with 6,968 unique Wi-Fi device connections, a 35 percent take rate from the sellout 19,796 fans on hand. According to the Atomic Data figures, the stadium’s Wi-Fi network saw peak Wi-Fi bandwidth usage of 1.9 Gbps on that opening day; of the 85 GB Wi-Fi data total, download traffic was 38.7 GB and upload traffic was 46.3 GB.
According to Wright, the stadium has already had several visits from representatives from other clubs, who are all interested in the networking technology. Wright’s advice to other clubs who are in the process of thinking about or building new stadiums: You should get on the horn with Atomic Data.
“I tell them if you’re from Austin or New England, you should be talking to Atomic,” Wright said. “They should try to replicate the relationship we have with them.”