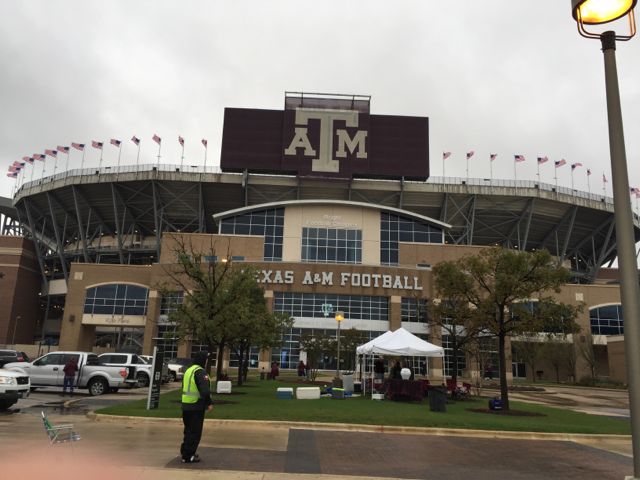
In fact, after reviewing loads of live network-performance data of Kyle Field’s new Wi-Fi and DAS in action, and after maxing out the top levels on our speed tests time after time during an informal walk-around on a game day, we’ve come to the conclusion that Kyle Field has itself a Spinal Tap of a wireless deployment. Meaning, that if other stadium networks stop at 10, this one goes to 11.
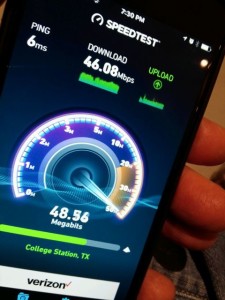
Movie references aside, quite simply, by the numbers Kyle Field’s wireless network performance is unequaled by any other large public venue’s we’ve tested in terms of raw speed and the ability to deliver bandwidth. With DAS and Wi-Fi speed measurements ranging between 40 Mbps and 60+ Mbps pretty much everywhere we roamed inside the 102,512-seat venue, it’s a safe bet to say that the school’s desire to “build the best network” in a stadium hit its goal as best as it could.
Editor’s note: This story is part of our most recent STADIUM TECH REPORT, the COLLEGE FOOTBALL ISSUE. The 40+ page report, which includes profiles of stadium deployments at Texas A&M, Kansas State, Ole Miss and Oklahoma, is available for FREE DOWNLOAD from our site. Get your copy today!
On one hand, the network’s top-line performance is not that much of a surprise, since as part of an overall Kyle Field renovation that has already cost an estimated $485 million, the optical-based Wi-Fi, DAS and IPTV deployment inside the Aggies’ football palace is probably among the most expensive and expansive in-venue networks ever built. According to Phillip Ray, Vice Chancellor for Business Affairs at The Texas A&M University System, the total cost of the optical-based Wi-Fi, DAS and IPTV network was “somewhere north of $20 million.”
And even though the nation’s biggest cellular carriers, AT&T and Verizon Wireless, paid nearly half the network’s cost – $10 million, according to Ray – with the dedication and work crews brought to the table by main suppliers IBM and Corning, and Wi-Fi gear vendor Aruba, you have components, expertise and budgetary freedom that perhaps only a small group of venue owners could hope to match.But just throwing money and technology at a stadium doesn’t necessarily produce a great network. In a venue the size of the new Kyle Field there needs to be great care and innovative thinking behind antenna placement and tuning, and in that arena Texas A&M also had the guiding hand of AmpThink, a small firm with oversized smarts in Wi-Fi deployment, as evidenced by its impressive track record of helping wireless deployments at the biggest events including several recent Super Bowls.
The core decision to go with optical for the network’s guts, and a tactical decision to put a huge chunk of the Wi-Fi APs in under-seat deployments are just part of the strategy that produced a network that – in A&M fan parlance – can “BTHO” (Beat The Hell Out) of most challengers.
Since it’s almost impossible to directly compare stadiums and venue network performances due to all the possible variables, you’ll never hear us at Mobile Sports Report declare a “champion” when it comes to click-bait themes like “the most connected stadium ever.” Given its remote location some three hours south of Dallas in College Station, Texas, Kyle Field will almost certainly never face the ultimate “big game” pressures of a Super Bowl or a College Football Playoff championship, so the network may never know the stress such large, bucket-list gatherings can produce. And so far, there aren’t many ambitious fan-facing applications that use the network, like in-seat food delivery or wayfinding apps found in other stadiums.
But as part of the football-crazy SEC, and as the altar of pigskin worship for some of the most dedicated fans seen anywhere, Kyle Field is sure to see its share of sellout contests against SEC rivals that will push wireless usage to new heights, especially as more fans learn about and use the still-new system. Though total Wi-Fi usage at the Nov. 7 game we attended versus Auburn (a 26-10 Texas A&M loss) was “only” 2.94 terabytes – a total hampered by cold, windy and rainy conditions – an Oct. 17 game earlier in the season against Alabama saw 5.7 TB of Wi-Fi usage on the Kyle Field network, a number surpassed only by last year’s Super Bowl (with 6.2 TB of Wi-Fi use) in terms of total tonnage.
At the very least, the raw numbers of total attendees and the obvious strength of the still-new network is sure to guarantee that Kyle Field’s wireless deployment will be one of the most analyzed stadium networks for the foreseeable future.
What follows are some on-the-spot observations from our visit, which was aided by the guidance and hospitality of Corning project manager Sean Heffner, who played “tour guide” for part of the day, giving us behind-the-scenes access and views of the deployment that are unavailable to the general fan audience.An off-campus DAS head end
This story starts not inside Kyle Field, but in a section of town just over three miles away from the stadium, on a muddy road that curves behind a funky nursery growing strange-looking plants. A gray metal box, like a big warehouse, is our destination, and the only clue as to what’s inside is the big antenna located right next to it. This structure is the Kyle Field DAS head end, where cellular carrier equipment connects to the fiber network that will bring signals to and from fans inside the stadium.
Why is the head end so far away? According to Corning’s Heffner there was no room for this huge space inside the stadium. But thanks to the use of optical fiber, the location is not a problem since signals traveling at the speed of light makes 3.3 miles an insignificant span.
It might be helpful to back up a bit if you haven’t heard the full story of the Kyle Field deployment, which we told last year when the job was halfway completed. Though the rebuilding of the stadium was started with copper-based networks as the original plan, a last-minute audible championed by Texas A&M chancellor John Sharp sent the school on a decidedly untraditional path, by building a stadium network with a single optical-based core for Wi-Fi, DAS and IPTV networks. The kicker? Not only would this network have huge capacity and be future-proof against growth, it would actually cost less than a comparable copper-based deployment. If it got built on time, that is.
Though the pitch for better performance, far more capacity, use of less space, and cheaper costs might sound a bit too good to believe, most of it is just the combination of the simple physics advantages of using fiber over copper, which are well known in the core telecom and large-enterprise networking worlds, applied to a stadium situation.
Without going too deeply into the physics or technology, a simple explanation of the benefits stem from the fact that optical fiber can carry far more bandwidth than copper, at farther distances, using less power. Those advantages are why fiber is used extensively in core backbone networks, and has been creeping slowly closer to the user’s destination, through deployments like Verizon’s FiOS.And that’s also the reason why Texas A&M could put its DAS head end out in a field where it’s easier to add to (no space constraints), because the speed of fiber makes distance somewhat irrelevant. Corning’s Heffner also said that the DAS can be managed remotely, so that staff doesn’t need to be physically present to monitor the equipment.
Of course, there was the small matter of digging trenches for optical fibers to get from the head end to the stadium, but again, for this project it is apparent that getting things done was more important than strictly worrying about costs. Beyond the cash that the carriers all put in, other vendors and construction partners all put in some extra efforts or resources – in part, probably because the value of positive publicity for being part of such an ambitious undertaking makes any extra costs easy to justify.
Keeping the best fans connected and happy
From the head end, the fiber winds its way past apartment buildings and a golf course to get to Kyle Field, the center of the local universe on football game days. Deep inside the bowels of the venue is where the fiber meets networking gear, in a room chilled to the temperature of firm ice cream. Here is where the human element that helps keep the network running spends its game days, wearing fleece and ski jackets no matter what the temperature is outside.
In addition to Corning, IBM and AmpThink employees, this room during our visit also had a representative from YinzCam in attendance, a rarity for a company that prides itself on being able to have its stadium and team apps run without local supervision. But with YinzCam recently named as a partner to IBM’s nascent stadium technology practice, it’s apparent that the Kyle Field network is more than just a great service for the fans in the seats – it’s also a proof of concept network that is being closely watched by all the entities that helped bring it together, who for many reasons want to be able to catch any issues before they become problems.How big and how ambitious is the Kyle Field network? From the outset, Corning and IBM said the Wi-Fi network part was designed to support 100,000 connections at a speed of 2 Mbps, so that if everyone in the stadium decided to log on, they’d all have decent bandwidth. But so far, that upper level hasn’t been tested yet.
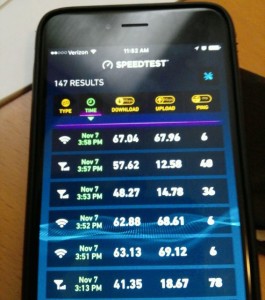
What happened through the first season was a “take rate” averaging in the 35,000-37,000 range, meaning that during a game day, roughly one-third of the fans in attendance used the Wi-Fi at some point. The average concurrent user peaks – the highest numbers of fans using the network at the same time – generally averaged in the mid-20,000 range, according to figures provided by Corning and AmpThink; so instead of 100,000 fans connecting at 2 Mbps, this season there was about a quarter of that number connecting at much higher data rates, if our ad hoc speed tests are any proof.
Our first test that Saturday [Nov. 7, 2015], just inside a lower-level service entryway, hit 41.35 Mbps for download and 18.67 on the upload, on a Verizon iPhone 6 Plus over the stadium’s DAS. And yes, that download speed was the slowest we’d record all day, either on the DAS or the Wi-Fi.
Inside the control room we spent some time with AmpThink CEO Bill Anderson, who could probably use up an entire football game talking about Wi-Fi network deployment strategies if he didn’t have a big network to watch. On this Saturday the top things we learned about Kyle Field is that Anderson and AmpThink are solid believers in under-seat AP placements for performance reasons; according to Anderson at Kyle Field, fully 669 of the stadium’s 1,300 APs can be found underneath seats. Anderson also is a stickler for “real” Wi-Fi usage measurements, like trying to weed out devices that may have autoconnected to the Wi-Fi network but not used it from the “unique user” totals – and to take bandwidth measurements at the network firewall, to truly see how much “live” bandwidth is coming and going.
AmpThink’s attention to detail includes deploying and configuring APs differently depending on which section they are located in – student sections, for example, are more densely packed with people than other sections so the APs need different tuning. Corning’s Heffner also said that the oDAS – the DAS just outside the stadium – got special attention due to the large numbers of tailgating fans, both before and during the games. At the Alabama game, Heffner said there were some 30,000 fans who remained outside the stadium during the contest, never coming inside but still wanting to participate in the scene.AmpThink, Corning, IBM and others involved at Kyle Field all seem keen on finding out just how much bandwidth stadium fans will use if you give them unlimited access. The guess? According to Corning’s Heffner, the mantra of stadium networks these days seems to be: “If you provide more capacity, it gets consumed.”
The ‘real’ 12th man
After walking through a tunnel with a nearly full cable tray overhead (“It’d be even more loaded if we were using copper,” Heffner said) we went out into the stadium itself, which was just starting to fill. Though the overcast day and intermittment rain squalls might have kept other teams’ fans from showing up for a 5:30 p.m. local start time, that simply wasn’t the case at an A&M home game.
As someone who’s attended a countless number of football games, small and large – including a Super Bowl and last year’s inaugural College Football Playoff championship game – I can honestly say that the level of fan participation at Texas A&M is like nothing I’d seen before. The student section alone spans two decks on the stadium’s east side and takes up 40,000 seats, according to stadium officials – simply dwarfing anything I’d ever witnessed. (Out of an enrollment of 57,000+, having 40,000 students attend games is incredible.) And outside of small high school crowds I’d never seen an entire full stadium participate in all the school songs, the “yells” (do NOT call them “cheers” here) and the locked-arms back-and-forth “sawing” dance without any need for scoreboard instruction.Part of the stadium renovation that closed the structure into a bowl was, according to school officials, designed to make Kyle Field even more intimidating than it already was, by increasing the sound levels possible. Unfortunately the night of our visit some early Auburn scores took some of the steam out of the crowd, and a driving, chilling rain that appeared just before halftime sent a good part of the crowd either home or into the concourses looking for warmth and shelter. (The next day, several columnists in the local paper admonished the fans who left early for their transgressions; how dare they depart a game whose outcome was still in doubt?)
But I’ll never forget the power of the synchronized “yells” of tens of thousands of fans during pregame, and the roar that surfaced when former Aggie QB Johnny Manziel made a surprise appearance on the field before kickoff. Seattle Seahawks fans may stake the pro claim to fan support, but if you want to determine the “real” 12th man experience you need to stop by Kyle Field and give your ears a taste of loud.
Controlling the TV with the app
If the students and alumni and other fans outside provide the vocal power, the money power that helped get the stadium rebuilt can be found in the new Kyle Field suites and premium seating areas, some of which are found on the venue’s west side, which was blown up last December and rebuilt in time for this past season.
Inside the All American Club – a behind-the-walls gathering area with catered food and bars that would not seem out of place in Levi’s Stadium or AT&T Stadium – we tested the Wi-Fi and got speeds of 63 Mbps down, 69 Mbps up; Verizon’s 4G LTE service on the DAS hit 48 Mbps/14.78 Mbps, while AT&T’s 4G LTE DAS checked in at 40 Mbps/22 Mbps.In an actual suite where we were allowed to check out the IPTV displays, the speed tests got 67/67 for Wi-Fi and 57/12 for Verizon 4G LTE. So the well-heeled backers of A&M football shouldn’t have any problems when it comes to connectivity.
As for the IPTV controls, the new system from YinzCam solves one of the problems that’s plagued stadium suites since there’s been suites: What do you do with the TV remote? What YinzCam did for Texas A&M was link the TV controls to a Texas A&M “TV Remote” app; by simply punching in a numerical code that appears on the bottom of the screen in front of you, anyone with access to a suite or club area with TVs can change the channel to a long list of selections, including multiple live game-day views (stadium screen, broadcast view) as well as to other channels, like other games on the ESPN SEC network.
By having a static code number for each TV and another set of numbers that randomly scrambles over time, the system smartly builds security into the channel changing system, and prevents someone who had been in a suite previously from being able to change the channels after they leave. The whole remote-control process took less than a minute to learn, and we had fun wandering through the club-level areas our pass gave us access to, changing screens as we saw fit.
Our favorite places to watch the game at Kyle Field were the loge-level lounges, where you could first purchase food and beverages, including alcoholic ones, at an inside bar and then sit at an outside seat with a small-screen TV in front of you for information overload. The Wi-Fi in the southwest corner loge lounge checked in at 67.03/62.93, so it was no problem being connected via mobile device, either.
What comes next for the Kyle Field network?
Even though the rain had started coming down harder, we left the comfort and warmth of the club levels to wander around the stadium’s upper decks, including the student section, where we watched numerous fans taking pictures or videos of the band’s halftime performance. Clearly most everyone in Kyle Field had gotten the message and wasn’t afraid that they won’t connect if they use their mobile device at the game, even among 102,000 of their closest friends.
The question now for Kyle Field is what does it do next with its network? The most obvious place for innovation or new features is with a stadium-centric app, one that could provide services like a wayfinding map. Maybe it was our round-the-stadium wandering that produced confusion finding our way around, but any building that seats 102,000 plus could use an interactive map. It might also be interesting to tie a map to concessions – the night we visited, there were long lines at the few hot chocolate stands due to the cold weather; in such situations you could conceivably use the network to find out where hot chocolate stands were running low, maybe open new ones and alert fans through the app.We’re guessing parking and ticketing functions might also be tied to the app in the future, but for now we’ll have to wait and see what happens. One thing in Kyle Field’s favor for the future: thanks to the capacity of the optical network buildout, the stadium already has thousands of spare fiber connections that aren’t currently being used. That means when it’s time to upgrade or add more DAS antennas, Wi-Fi APs or whatever comes next, Kyle Field is already wired to handle it.
For the Nov. 7 game at Kyle Field, the final numbers included 37,121 unique users of the Wi-Fi network, and a peak concurrent user number of 23,101 taken near the end of the 3rd quarter. The total traffic used on the Wi-Fi network that night was 2.94 TB, perhaps low or average for Kyle Field these days but it’s helpful to remember that just three years ago that was right around the total Wi-Fi data used at a Super Bowl.
Until the next IBM/Corning network gets built in Atlanta (at the Falcons’ new Mercedes-Benz Stadium, slated to open in 2017), the Kyle Field network will no doubt be the center of much stadium-technology market attention, especially if they ever do manage to get 100,000 fans to use the Wi-Fi all at once. While A&M’s on-the-field fortunes in the competitive SEC are a yearly question, the performance of the network in the Aggies’ stadium isn’t; right now it would certainly be one of the top four seeds, if not No. 1, if there was such a thing as a college stadium network playoff.
What we’re looking forward to is more data and more reports from a stadium with a network that can provide “that extra push over the edge” when fans want to turn their connectivity dial past 10. Remember, this one goes to 11. It’s one more.
(More photos below! And don’t forget to download your copy of the STADIUM TECH REPORT for more!)

Panoramic view of Kyle Field before the 102,000 fans fill the seats.
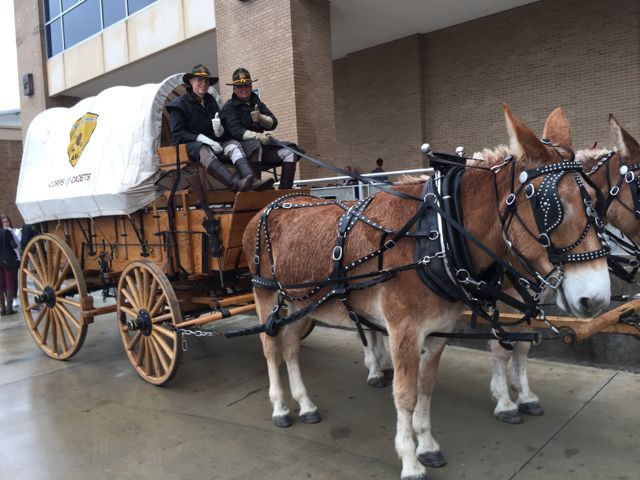

Some things at Kyle Field operate at ‘traditional’ speeds.
Outside the south gate before the game begins.
Overhang antenna in the middle section of the stadium.