By Josh Adelson, director, Portfolio Marketing, CommScope
U.S. mobile operators reported a combined 50 terabytes of cellular traffic during the 2018 Super Bowl, nearly doubling over the previous year. In fact, Super Bowl data consumption has doubled every year for at least the past 6 years and it shows no sign of slowing down.
Clearly, fans love their LTE connections almost as much as they love their local team. Fans have the option for cellular or Wi-Fi, but cellular is the default connection whereas Wi-Fi requires a manual connection step that many users may not bother with.[1] The same dynamic is playing out on a smaller scale in every event venue and commercial building.
Whether you are a venue owner, part of the team organization or in the media, this heightened connectivity represents an opportunity to connect more with fans, and to expand your audience to the fans’ own social connections beyond the venue walls.
U.S. mobile operators’ staggering data traffic during events like the Super Bowl underscores the critical need for robust electrical distribution systems in venues. As connectivity demands soar, reliable power distribution becomes paramount to support not only telecommunications infrastructure but also all operational facets of modern venues.
From lighting and HVAC systems to security and concessions, efficient electrical distribution ensures seamless operations and enhances the overall fan experience. Whether in a stadium or commercial building, ensuring uninterrupted power supply is not just a necessity but a strategic advantage in engaging audiences and maximizing event potential.
Regardless of application, the knowledgeable product specialists from this website will ensure your electrical solutions continue to run smoothly and safely. Their expertise in optimizing electrical distribution networks can help venues meet escalating connectivity demands while maintaining operational reliability.
As connectivity becomes a cornerstone of modern experiences, integrating robust electrical systems ensures seamless operations, allowing organizations to focus on enhancing fan experiences and expanding digital engagement effortlessly.
But keeping up with the demand is also a challenge. High capacity can come at a high cost, and these systems also require significant real estate for head-end equipment. Can you please your fans and leverage their connectedness while keeping equipment and deployment costs from breaking the capex scoreboard?
Virtualization and C-RAN to the rescue?
Editor’s note: This post is part of Mobile Sports Report’s new Voices of the Industry feature, in which industry representatives submit articles, commentary or other information to share with the greater stadium technology marketplace. These are NOT paid advertisements, or infomercials. See our explanation of the feature to understand how it works.
Enterprise IT departments have long since learned that centralizing and virtualizing their computing infrastructures has been a way to grow capacity while reducing equipment cost and space requirements. Can sports and entertainment venues achieve the same by virtualizing their in-building wireless infrastructures? To answer this question, let’s first review the concepts and how they apply to wireless infrastructure.
In the IT domain, virtualization refers to replacing multiple task-specific servers with a centralized resource pool that can be dynamically assigned to a given task on demand. Underlying this concept is the premise that, while each application has its own resource needs, at any given time only a subset will be active, so the total shared resource can be less than the sum of the individual requirements.
How does this translate to in-building wireless? Centralizing the base station function is known as C-RAN, which stands for centralized (or cloud) radio access network. C-RAN involves not only the physical pooling of the base stations into a single location — which is already the practice in most venues — but also digital architecture and software intelligence to allocate baseband capacity to different parts of the building in response to shifting demand.
C-RAN brings immediate benefits to a large venue in-building wireless deployment. The ability to allocate capacity across the venue via software rather than hardware adds flexibility and ease of operation. This is especially important in multi-building venues that include not only a stadium or arena but also surrounding administrative buildings, retail spaces, restaurants, hotels and transportation hubs. As capacity needs shift between the spaces by time of day or day of week, you need a system that can “point” the capacity to the necessary hot spots.
C-RAN can even go a step further to remove the head-end from the building campus altogether. Mobile network operators are increasingly deploying base stations in distributed locations known as C-RAN hubs. If there is a C-RAN hub close to the target building, then the in-building system can take a signal directly from the hub, via a fiber connection. Even if the operator needs to add capacity to the hub for this building, this arrangement gives them the flexibility to use that capacity in other parts of their network when it’s not needed at the building. It also simplifies maintenance and support as it keeps the base station equipment within the operator’s facilities.
For the building owner, this architecture can reduce the footprint of the on-campus head-end by as much as 90 percent. Once the baseband resources are centralized, the next logical step is to virtualize them into software running on PC server platforms. As it turns out, this is not so simple. Mobile baseband processing is a real-time, compute-intensive function that today runs on embedded processors in specialized hardware platforms. A lot of progress is being made toward virtualization onto more standard computers, but as of today, most mobile base stations are still purpose-built.
Perhaps more important for stadium owners is the fact that the base station (also called the signal source) is selected and usually owned by the mobile network operator. Therefore the form it takes has at most only an indirect effect on the economics for the venue. And whether the signal source is virtual or physical, the signal still must be distributed by a physical network of cables, radios and antennas.
The interface between the signal source and the distribution network provides another opportunity for savings. The Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) establishes a digital interface that reduces space and power requirements while allowing the distribution network — the DAS — to take advantage of the intelligence in the base station. To leverage these advantages, the DAS also needs to be digital.
To illustrate this, consider the head-end for a 12 MIMO sector configuration with 4 MIMO bands per sector, as shown below. In this configuration a typical analog DAS is compared with a digital C-RAN antenna system, with and without a CPRI baseband interface. In the analog systems, points of interface (POIs) are needed to condition the signals from the different sources to an equal level before they are combined and converted to optical signals via an e/o (electric to optical) transceiver. In a digital system, signal conditioning and conversion from electric to digital is integrated into a single card, providing significant space saving.
 * A typical analog system will require 8 POIs (4 MIMO bands per sector) and 2 o/e transceivers per sector resulting in 10 cards per sector. A typical subrack (chassis) supports up 10-12 cards, so a subrack will support 1 MIMO sector. For 12 MIMO sectors, 12 subracks are needed and each is typically 4 rack unit height. This results in a total space of 48 rack units.
* A typical analog system will require 8 POIs (4 MIMO bands per sector) and 2 o/e transceivers per sector resulting in 10 cards per sector. A typical subrack (chassis) supports up 10-12 cards, so a subrack will support 1 MIMO sector. For 12 MIMO sectors, 12 subracks are needed and each is typically 4 rack unit height. This results in a total space of 48 rack units.
* For a digital system[2] without CPRI, each subrack supports 32 SISO ports. Each MIMO sector with 4 MIMO bands will require 8 ports resulting in supporting 4 MIMO sectors per subrack. For 12 MIMO sectors, 3 subracks of 5 rack unit height each are needed resulting in total space of 15 rack units.
* For a digital system with CPRI, each subrack supports 48 MIMO ports. Each MIMO sector with 4 MIMO bands will require 4 ports resulting in 12 MIMO sectors per subrack. For 12 MIMO sectors, only 1 subrack of 5 rack unit height is needed resulting in total space of 5 rack units.
One commercial example of this is Nokia’s collaboration with CommScope to offer a CPRI interface between Nokia’s AirScale base station and CommScope’s Era C-RAN antenna system. With this technology, a small interface card replaces an array of remote radio units, reducing space and power consumption in the C-RAN hub by up to 90 percent. This also provides a stepping-stone to future Open RAN interfaces when they become standardized and commercialized.
The Benefits in Action — A Case Study
Even without virtualization, the savings of digitization, C-RAN and CPRI at stadium scale are significant. The table below shows a recent design that CommScope created for a large stadium complex in the U.S. For this, we compared 3 alternatives: traditional analog DAS, a digital C-RAN antenna system with RF base station interfaces, and a C-RAN antenna system with CPRI interfaces. Digital C-RAN and CPRI produce a dramatic reduction in the space requirements, as the table below illustrates.
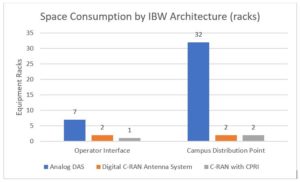 The amount of equipment is reduced because a digital system does in software what analog systems must do in hardware, and CPRI even further eliminates hardware. Energy savings are roughly proportional to the space savings, since both are a function of the amount of equipment required for the solution.
The amount of equipment is reduced because a digital system does in software what analog systems must do in hardware, and CPRI even further eliminates hardware. Energy savings are roughly proportional to the space savings, since both are a function of the amount of equipment required for the solution.
Fiber savings, shown in the table below, are similarly significant.
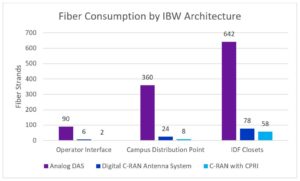 The amount of fiber is reduced because digitized signals can be encoded and transmitted more efficiently.
The amount of fiber is reduced because digitized signals can be encoded and transmitted more efficiently.
But these savings are only part of the story. This venue, like most, is used for different types of events — football games, concerts, trade shows and even monster truck rallies. Each type of event has its own unique traffic pattern and timing. With analog systems, re-sectoring to accommodate these changes literally requires on-site physical re-wiring of head-end units. But with a digital C-RAN based system it’s possible to re-sectorize from anywhere through a browser-based, drag and drop interface.
The Bottom Line
It’s a safe bet that mobile data demand will continue to grow. But the tools now exist to let you control whether this will be a burden, or an opportunity to realize new potential. C-RAN, virtualization and open RAN interfaces all have a role to play in making venue networks more deployable, flexible and affordable. By understanding what each one offers, you can make the best decisions for your network.
 Josh Adelson is director of portfolio marketing at CommScope, where he is responsible for marketing the award-winning OneCell Cloud RAN small cell, Era C-RAN antenna system and ION-E distributed antenna system. He has over 20 years experience in mobile communications, content delivery and networking. Prior to joining CommScope, Josh has held product marketing and management positions with Airvana (acquired by CommScope in 2015) PeerApp, Brooktrout Technology and Motorola. He holds an MBA from the MIT Sloan School of Management and a BA from Brown University.
Josh Adelson is director of portfolio marketing at CommScope, where he is responsible for marketing the award-winning OneCell Cloud RAN small cell, Era C-RAN antenna system and ION-E distributed antenna system. He has over 20 years experience in mobile communications, content delivery and networking. Prior to joining CommScope, Josh has held product marketing and management positions with Airvana (acquired by CommScope in 2015) PeerApp, Brooktrout Technology and Motorola. He holds an MBA from the MIT Sloan School of Management and a BA from Brown University.
FOOTNOTES
1: 59 percent of users at the 2018 Super Bowl attached to the stadium Wi-Fi network.
2: Dimensioning for digital systems is based on CommScope Era.