The front of Fiserv Forum, with the new Milwaukee Bucks logo ready for fan selfies. Credit all photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any photo for a larger image)
While MSR plans to circle back soon for some more in-depth reporting and live testing of the stadium’s Wi-Fi and DAS networks, and closer looks at the digital displays in action, our short tour of the Milwaukee Bucks’ new home made it clear that the designers and builders of Fiserv Forum definitely learned from what others had done before them, and then advanced things in many areas.
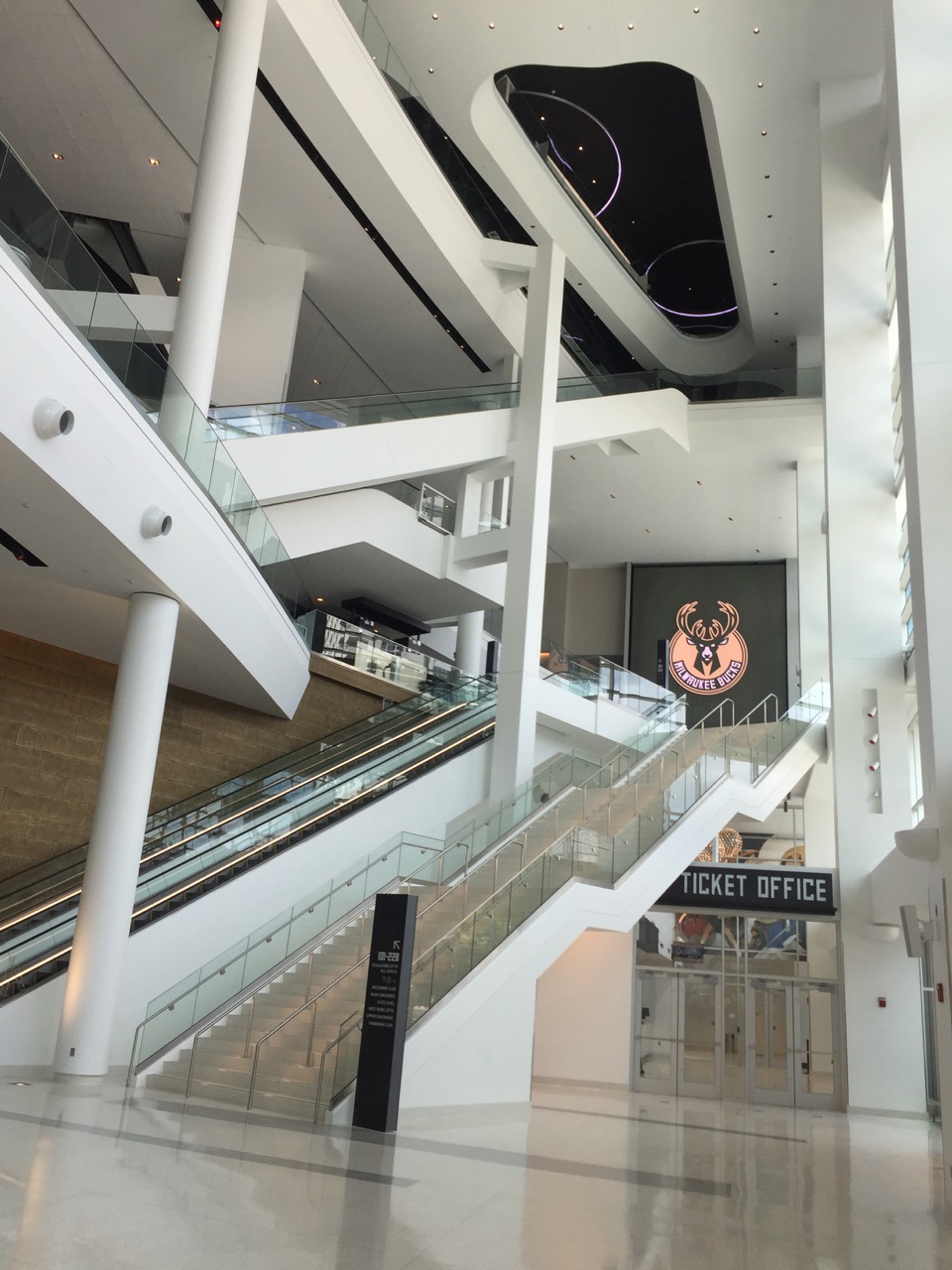
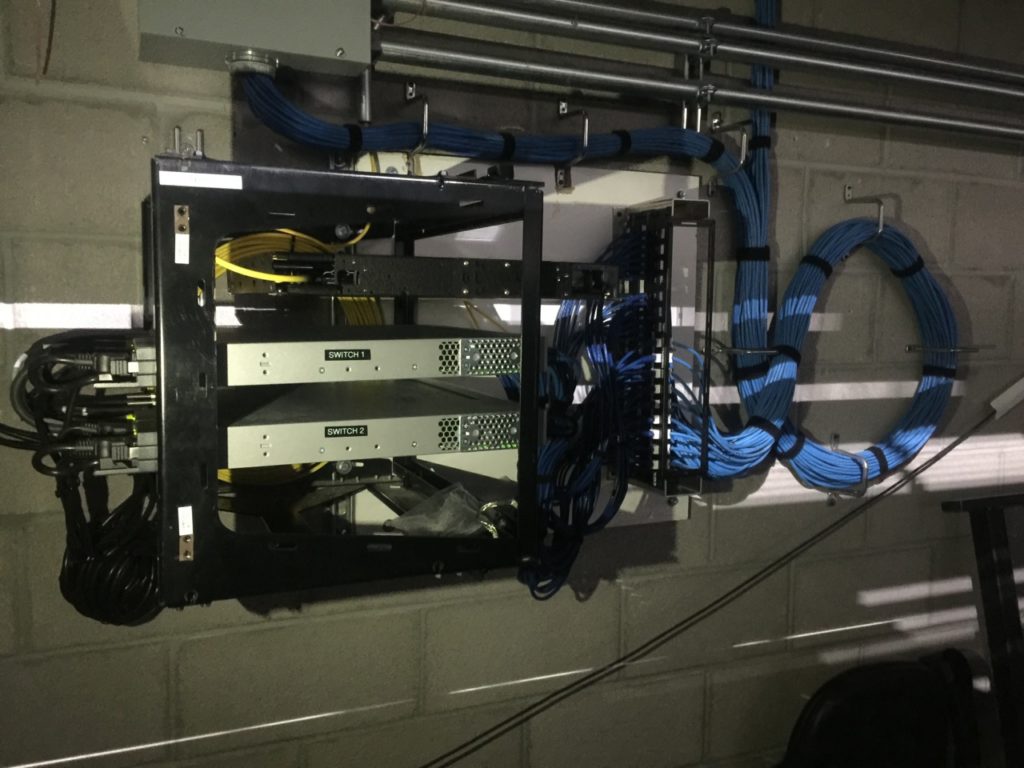
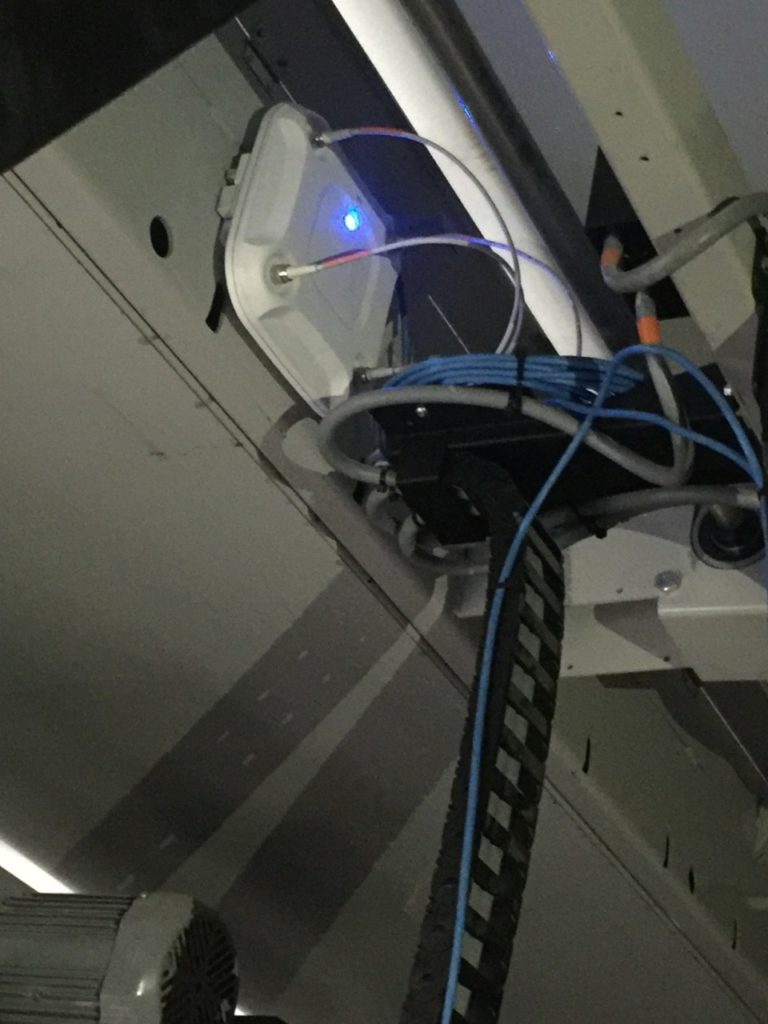
Smart touches on the networking side like small Wi-Fi antennas in the railings and clever use of overhead Wi-Fi enclosures as seating signage show a dual commitment to getting the tech right while also paying attention to aesthetics, sometimes a challenge that falls short on one side or the other. Other interesting twists include an array of TV screens and other displays underneath the main large video board, so that fans in courtside seats have their own comfortable way to view replays and other information.
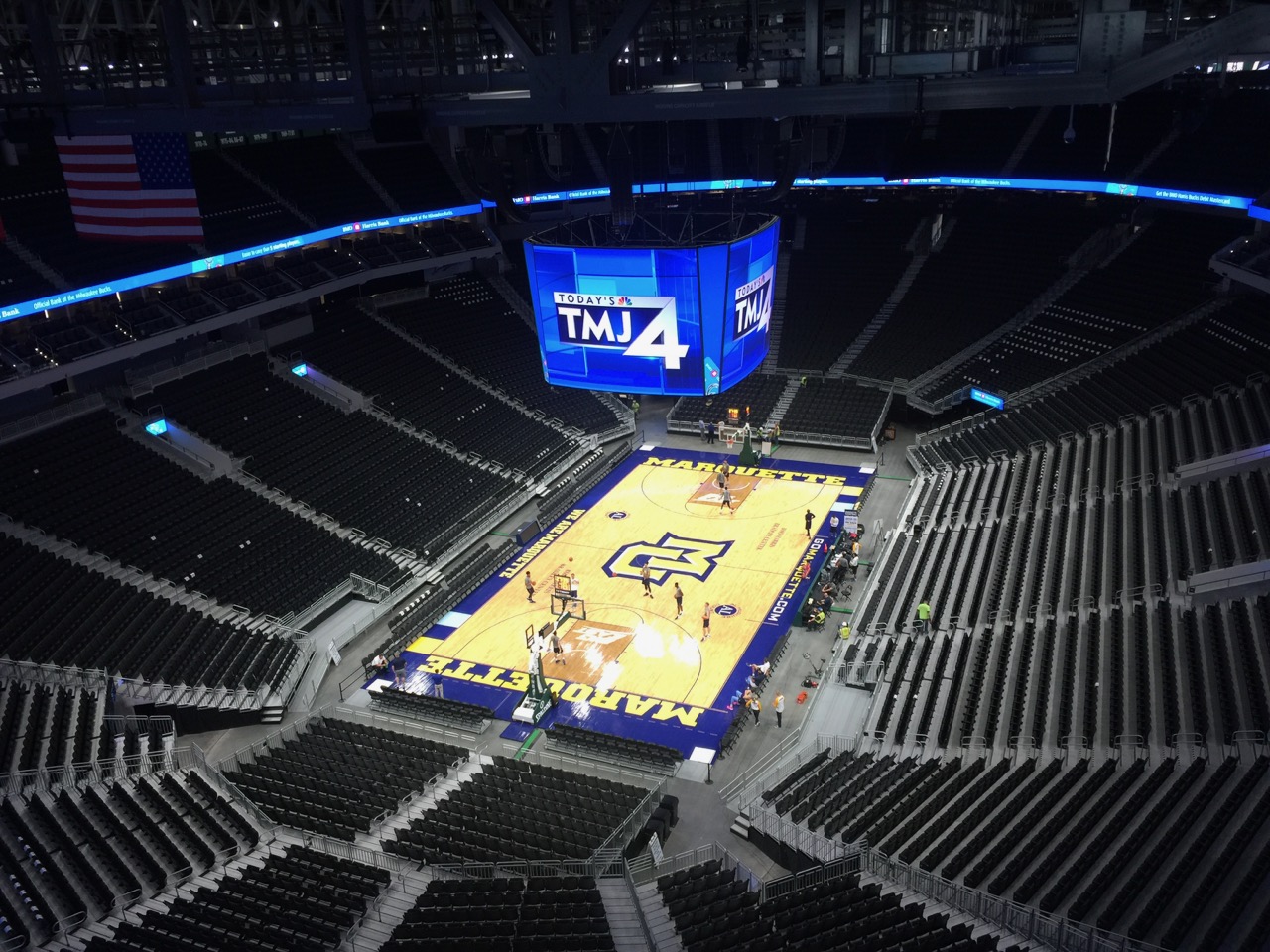
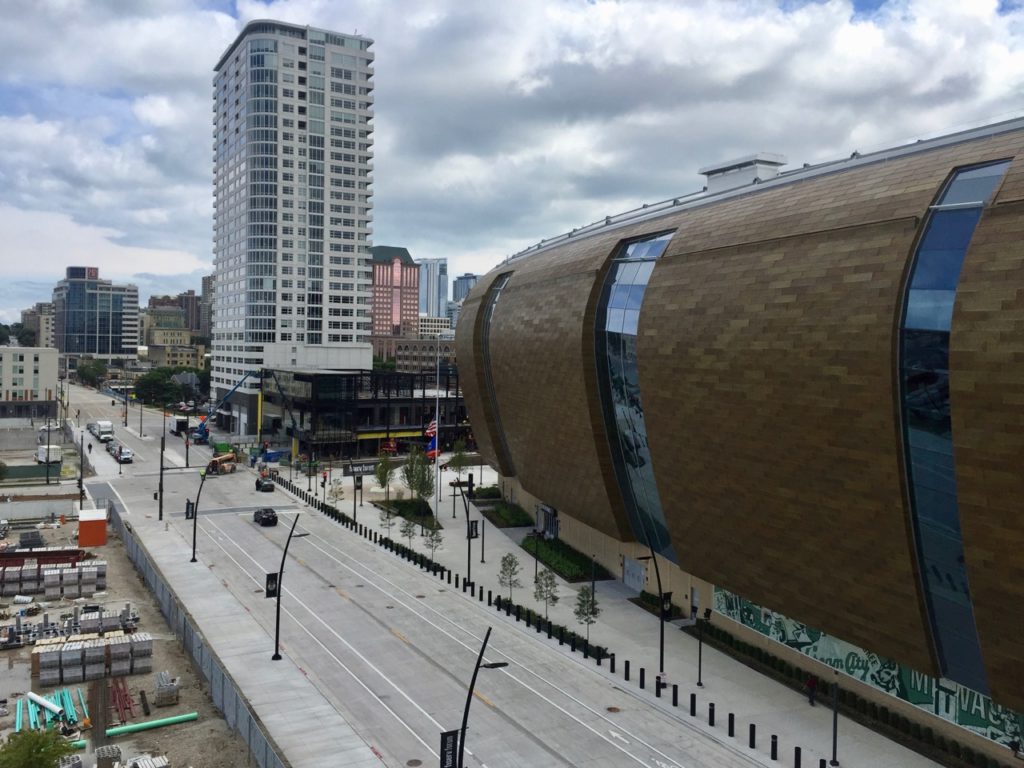
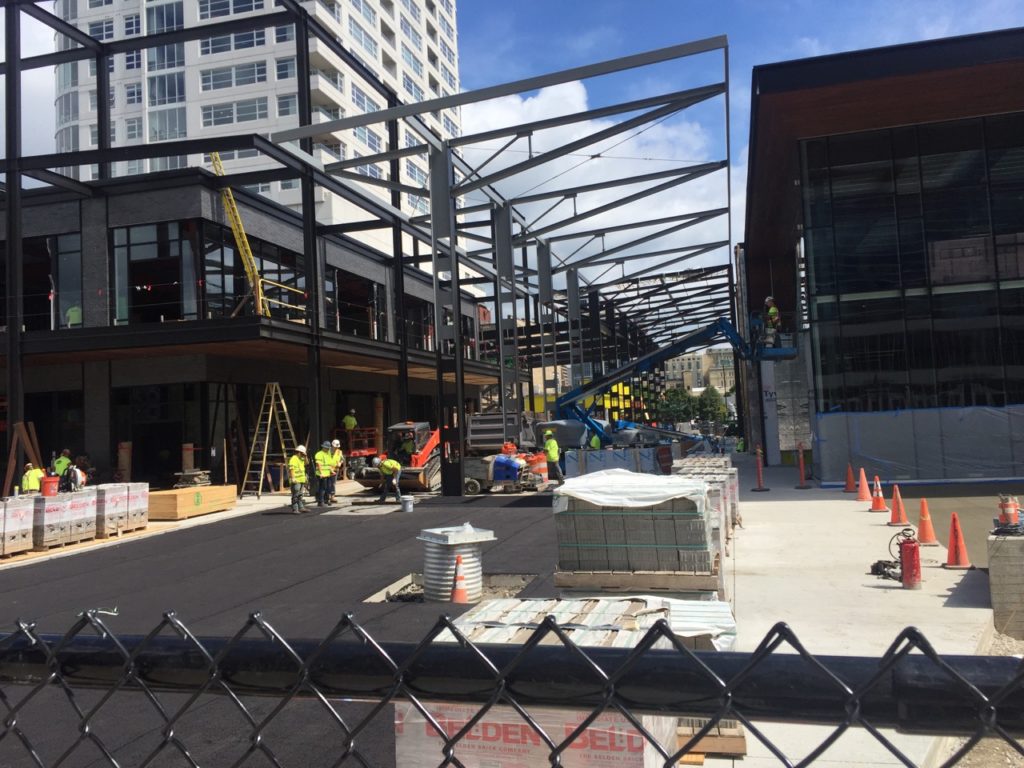
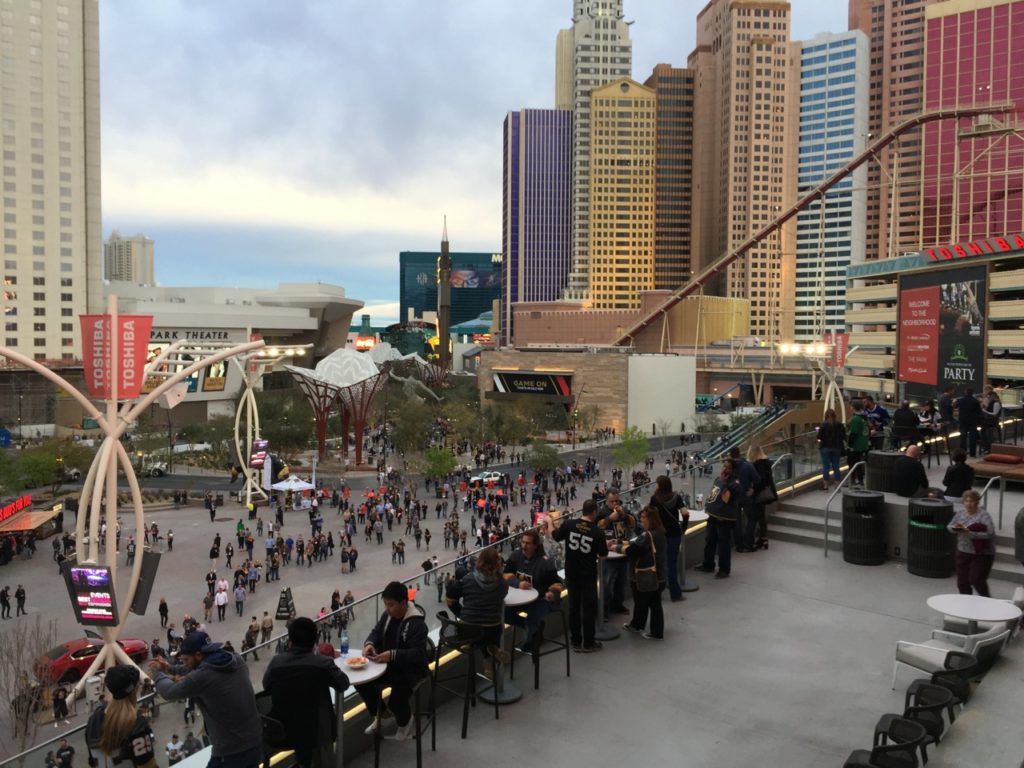
The visual fan experience at Fiserv Forum starts, of course, with the stadium’s unique outside design, which either looks like a breaking wave or part of a beer barrel, depending on your view and sense of artistic license. The venue also uses architectural twists to provide an assortment of exciting views, with the top-level Panorama Club giving any ticket holder an eagle’s-eye view of the court as well as a spectacular view to downtown Milwaukee, courtesy of an outside deck.Stay tuned for more MSR reporting on Fiserv Forum’s technology later this fall, including the Cisco Wi-Fi network with its 577 APs (most of which are the two-radio version) and Cisco Vision digital display deployment; cellular infrastructure from ExteNet and JMA; the LED banners and the huge Daktronics display; and live testing of the across-the-street beer garden scheduled to be open in time for Oktoberfest. Prosit and congrats to the Bucks and Fiserv. Some selected photos from our visit below (watch for more photos and more info in our upcoming Fall issue of the STADIUM TECH REPORT).
Artsy panoramic view of the front of Fiserv Forum
Inside the front door, the atrium soars up on both sides of the building
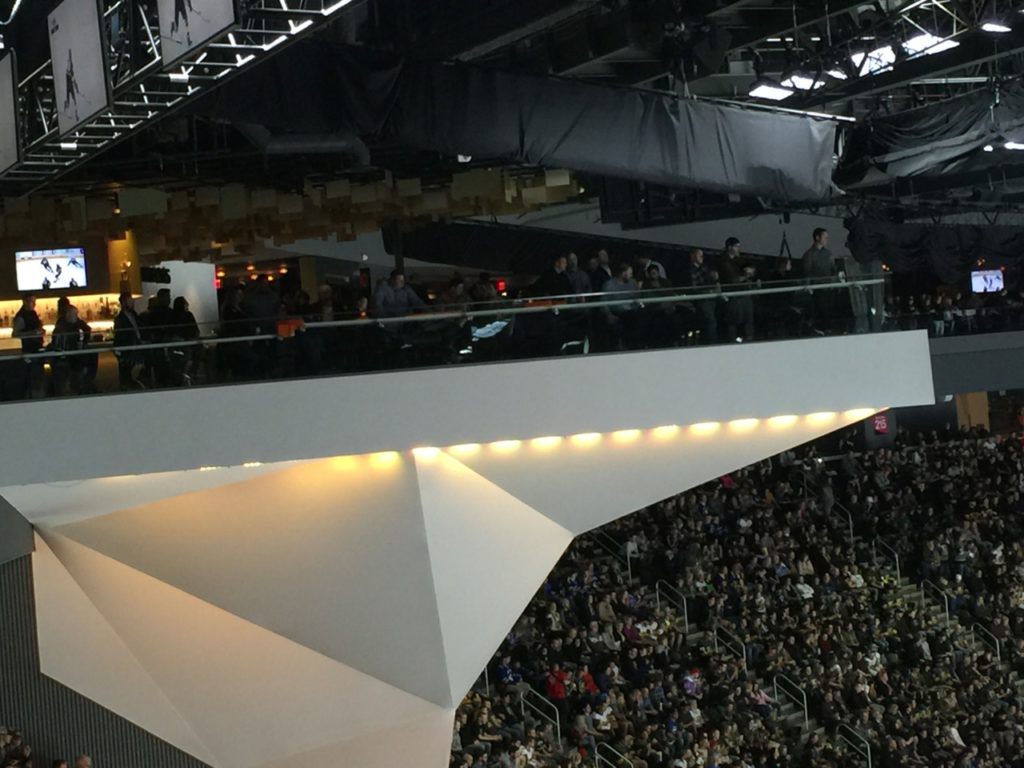
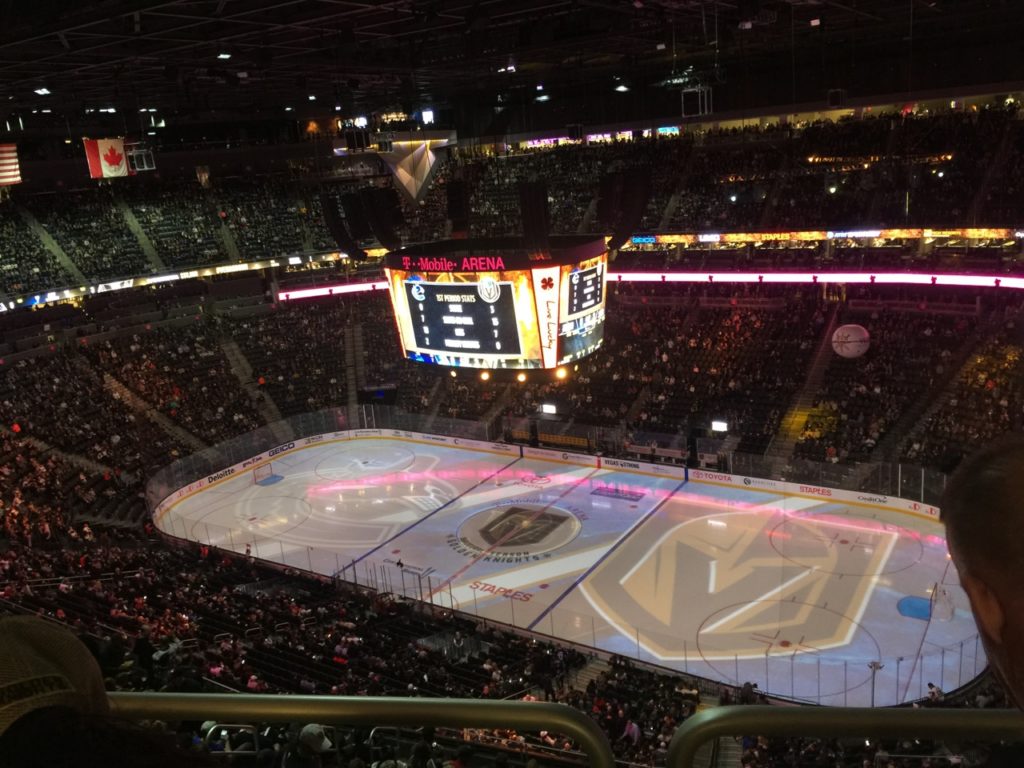
A full-court view from the Panorama Club (Marquette University will also use the stadium)
Looking up at the Panorama Club
The north side of the stadium, as seen from the attached parking structure
The section number sign doubles as a Wi-Fi AP enclosure
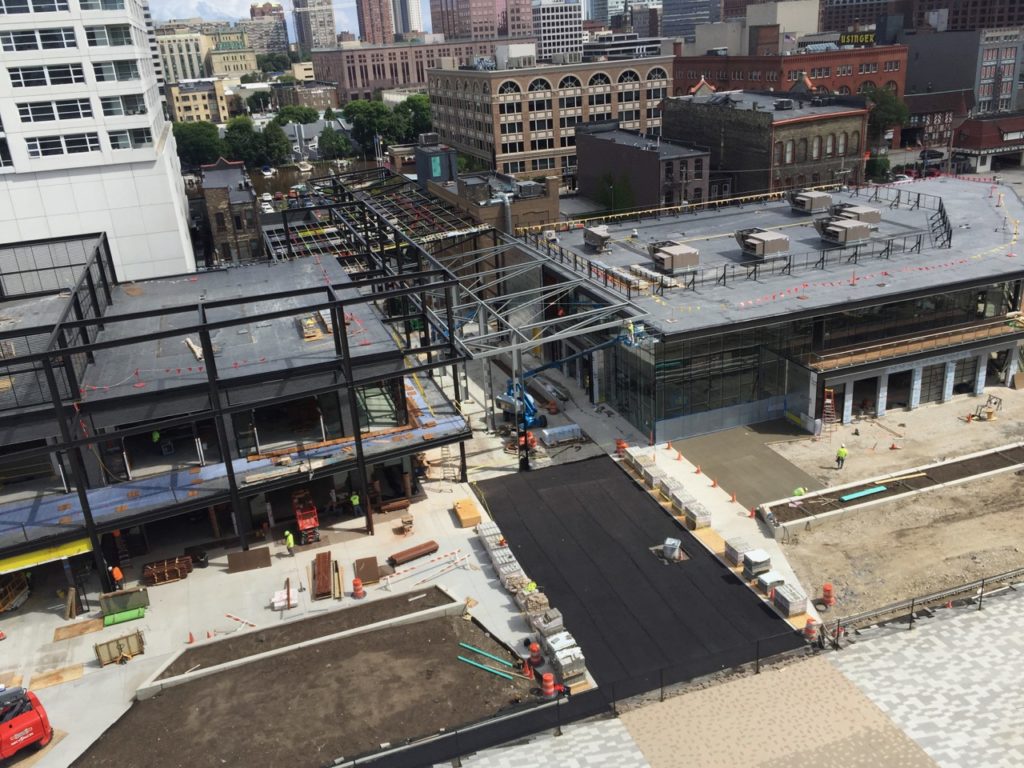
Construction continues on the next-door beer garden and entertainment area
View of the beer garden and entertainment area from the Panorama Club outside deck. The front two structures will house a brewpub and a Punch Bowl Social outlet
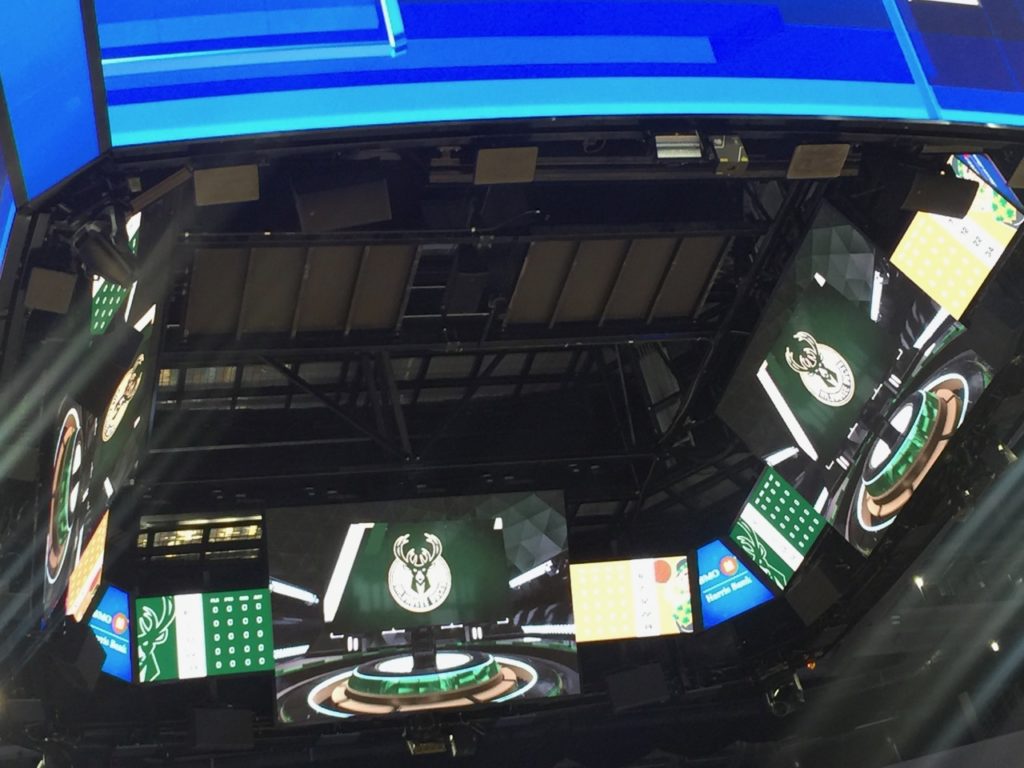
A look at the display (and wireless) technology mounted underneath the main video board
Concession displays
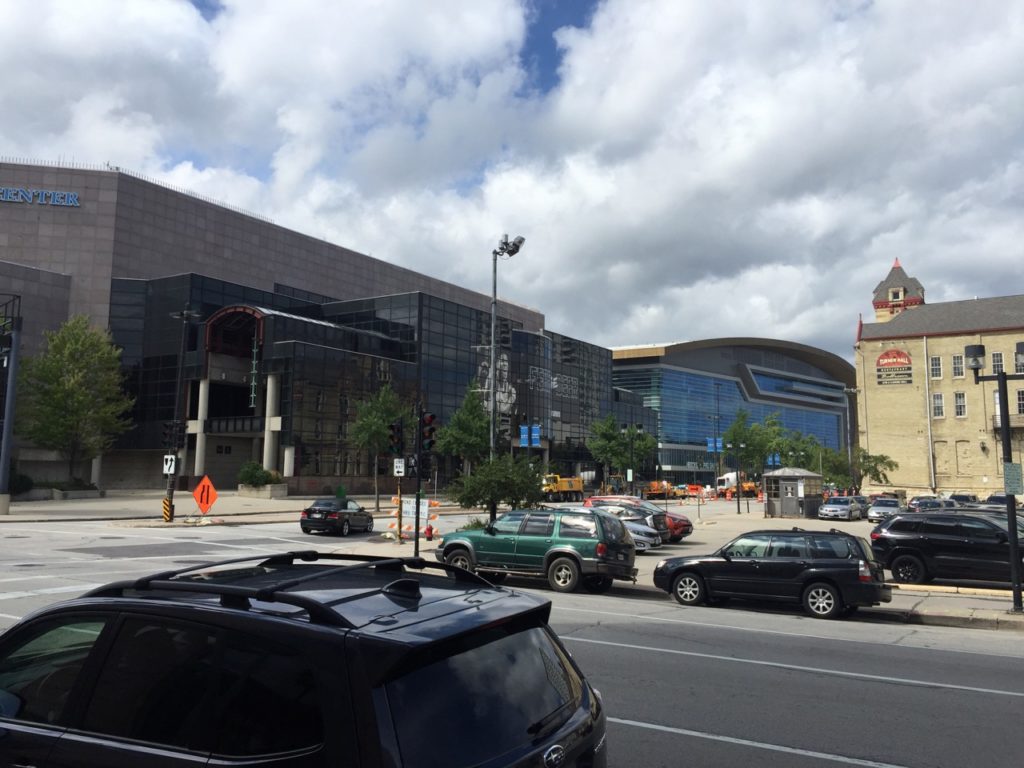
The Bradley Center, left, will soon be demolished, ceding the stage to Fiserv Forum
Fear the deer, but enjoy the beer