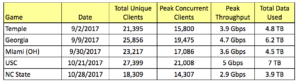
The LVCC’s Wi-Fi network, which was upgraded 3 years ago, has more than 2,000 Cisco Wi-Fi access points spread through the large halls where most of the CES activity takes place. According to stats compiled by Cox, the average connection time per device was 2 hours, and the network saw peak download throughput speeds of 1.72 Gbps and peak upload speeds of 1.13 Gbps.
We don’t have stats yet on DAS use at CES, but attendees at the LVCC may also have noticed a new LED welcome screen in the main hallway — enclosed below is a cool time-lapse video showing its (fast!) construction in time for the big event.