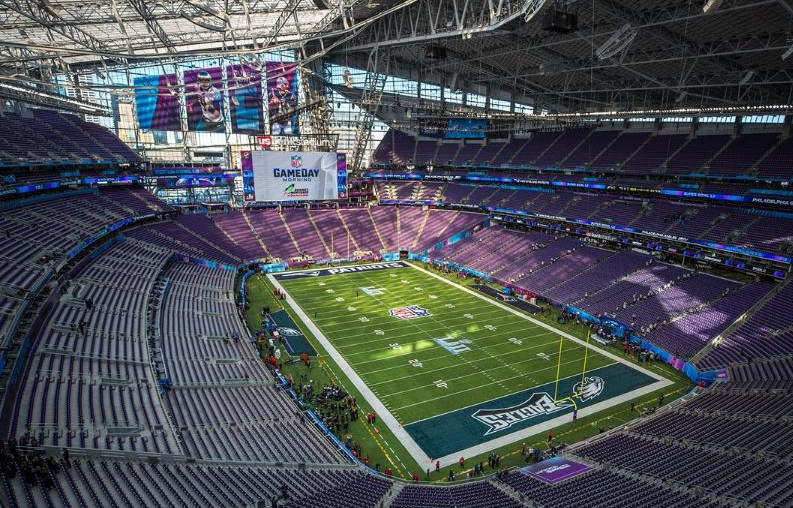
Hard Rock Stadium in Miami is using signage messages to help fans stay socially distanced. Credit: Miami Dolphins
And if keeping fans farther apart from each other is one of the simplest and best methods of enabling safer gatherings, it makes sense that many venues and technology and service providers are currently concentrating on venue entry and concession operations, with an eye toward using technology and procedures to cut down or eliminate the long lines that have long been a part of a game-day experience.
Before the pandemic changed events forever, many venues and fans were stuck in the systems and practices that had been the same for decades. While some forward-looking venues were experimenting with innovative digital technologies for entry and concessions operations, most were still caught somewhere in between the past and the future, with a mix of digital ticketing, paper tickets, cash transactions for parking and concessions, and bottleneck walkway traffic situations often caused by the random geography of stadiums, some built as long as 100 years ago. Fan behavior often contributed to these crowded situations, with the last-minute crush of entries from people who stayed at tailgate gatherings until just before kickoff a somewhat unwanted tradition at many stadiums across the country. But now, all that has changed.
The forced changes of Covid
In a wide series of interviews with venue owners and operators, team representatives, and technology manufacturers and service providers, we’ve seen general agreement with the idea that many of the “old ways of doing things” at events will no longer be possible as the pandemic continues, and most likely even after it subsides from its current critical state. Going forward, events in large public venues will need to adopt technologies and procedures aimed at not just keeping fans safe, but also to make them feel safe, and confident that the stadium operation is doing all it can in those regards.
The two areas of operations we are focusing on with this story are the two that easily account for the high- est potential of long lines: Stadium entry, and concessions. While historically these two operations have been fan-experience pain points in almost every venue, the good news is that mature technologies already exist to help solve for problems in both areas – and some best practices have already emerged from forward-looking venues and providers who embraced these ideas prior to the pandemic. What follows is a look at some of the technologies and services available for entry and concessions operations, with insights from early adopters and from the companies involved in the deployments.
Digital tickets and faster scanning
Editor’s note: This story is from our recent STADIUM TECH REPORT Fall 2020 issue, which you can read right now, no email or registration required! Also in this issue are profiles of the technology behind two of the most innovative venues to ever open, SoFi Stadium in Los Angeles and Allegiant Stadium in Las Vegas! START READING NOW!
Just like when airline ticketing went from printed paper to mostly mobile-device systems, so has the stadium and event entry business been changing. Prior to the pandemic, most venues of any size had at least some kind of digital ticketing system in place, with many moving to digital-only processes over the past few years. While there were still some holdouts, most of the people we interviewed agreed that the desire to make activities like parking lot and stadium entry faster and contact-free is now driving venues to adopt digital ticketing at a rapid pace.
“The tone has completely changed,” said Karri Zaremba, who until recently was chief operating officer at stadium app developer Venuetize (Zaremba is now a senior vice president with Major League Baseball, for ballpark experience and ticketing). According to Zaremba, this past summer teams and venues were showing “an eagerness and hunger” for digital ticketing systems that Venuetize hadn’t seen before.
“Everyone is scrambling to figure out a plan to reform venues and remove humans from the [interaction] equation,” Zaremba said.
George Baker, founder and CEO of parking technology provider ParkHub, agreed that the need to reduce hand-to-hand or face-to-face transactions is driving more technology in venue entry, beginning at the gate to the parking lot. ParkHub, which recently signed a deal with venue management firm Spectra to provide parking-lot technology to Spectra-managed properties, also raised an additional $15 million in venture funding this spring to help accelerate its business.

Parking attendants can scan digital tickets, a safer and faster alternative than cash. Credit: ParkHub
“For venues, it’s no longer a nicety, it’s a necessity,” said Baker of digital transactions.
One venue that has made a name for itself by its use of innovative fan-facing technology is the Los Angeles Football Club’s Banc of California Stadium, which opened in 2018. Christian Lau, chief technology officer for Major League Soccer’s LAFC, said contact-free entry and transactions have always been a part of the venue’s plan.
In fact, before the pandemic started the club was working with security technology provider Patriot One to help develop a new entry-gate system that would include innovations including eliminating the need for the single-person metal detectors as well as future support for entry via facial recognition technology. LAFC is using entry gate technology from Axess, a Salzburg, Austria- based provider.
“It is all part of redefining our great fan experience, and redefining the security stack,” said Lau. “We want to let you walk into the stadium like you’re walking into a Target store.”
Other venues, including the University of Oklahoma, are already borrowing from the airline playbook, by putting in more self-scanning ticket kiosks. The NFL’s Jacksonville Jaguars, one of the first pro football teams allowing fans to attend in limited numbers, said they have installed new metal detectors that allow fans to keep things like keys and cell phones in their pockets when entering. Kim Rometo, vice president and CIO for the Miami Dolphins, said that Miami’s Hard Rock Stadium now has “walk-through, multi-zone metal detectors” that let fans keep items in their pockets to speed up entry.
Temperature scans are a costly addition
One technology that got a lot of attention this summer was thermal detection devices, usually cameras that could scan people to detect a high body temperature, one of the signs of a possible Covid-19 infection. While such cameras are already in use in some places like airports, we have yet to find a major U.S. sports venue that has committed to installing thermal cameras for fan entry. The reason why? A combination of high costs (each scanner device can cost $10,000 or more) and unclear results, especially when used in large-scale operations like fans coming in to an event.
While many sports teams are using thermal detection devices to help keep staff and players safe as they enter team buildings and the stadiums, the prospect of trying to extend those operations to thousands of fans is a problem that requires an extra level of operational procedures. Chip Swisher, director in the smart solutions practice at CenturyLink, said venues looking to install thermal detection systems need to consider placement (since the cameras do not work as well in bright sunlight) and other mitigating factors, like fans just getting hot from being in the sun at a tailgate party. Teams will also need to develop procedures on how to handle fans who do show a high temperature, either with cooling tents (where they can be re-tested after a short time period) or with further testing or ways to refuse entry.
At some venues temperature checks are being performed, by staff members with handheld devices, a process that may possibly introduce more safety issues than it solves by forcing the person-to-person proximity. For most venues, the temperature-check process is currently a “wait and see” item, as they monitor what other venues are doing and what, if any, requirements for temperature checks are made by local governent or health officials.
Spacing and timed entry and departure
If television views of some of the first games with fans allowed in the stands are any proof, the idea of keeping fans spaced far apart in the stands seems to be working, except at some college games where students apparently violated safety precautions by massing together once inside the venue, often without masks.
For most teams that are starting to allow fans into stadiums, the digital ticket and the team or stadium application is the primary vehicle for keeping fans at safe distances when they enter and stay at the venue.
“We stretched existing solutions to meeting the need [for distancing],” said the Dolphins’ Rometo. “Ticketmaster introduced the ability to define seating pods for social distance and space them six feet from one another. We [also] program the digital tickets to display the preferred gate for social distancing along with a specific entry time. All social distancing signage will be displayed on Cisco Vision throughout the concourses and we augmented eight LED boards at entrances to communicate entrance times.”
While some venues have floated the idea of having set departure times, Rometo said that at Hard Rock Stadium fans can leave at any time they choose. If they stay until the end, she said, ushers will try to dismiss rows in an order to keep social distancing – but added that the space available inside the venue should keep crowds from forming.
“Hard Rock Stadium can hold more than 65,000 so we fully expect dismissing 13,000 will still occur in a timely fashion,” said Rometo of the team’s expected early attendance allowance.
And while some teams are eliminating tailgating completely, others like the Kansas City Chiefs are implementing spacing protocols in the parking lots, with every other space blocked off so that fans can’t park side by side.
Concessions: Lessons learned from retail, fast food
If there was one place in many stadiums that needed an overhaul even before the pandemic, it was concessions. According to Moon Javaid, chief strategy officer for the San Francisco 49ers, customer experience surveys have consistently shown concessions to be “the lowest-rated aspect” across all sports.
Anothy Perez, CEO of stadium app developer VenueNext, explained why that experience has been poor at so many venues for so long.

New kiosks from Appetize will be used in the Green Bay Packers’ Lambeau Field when it allows fans back in. Credit: Appetize
But the advent of the Covid-19 pandemic, Perez said, “gives you cover to try something new. It’s a paradigm shift.”
With her Venuetize hat on, Zaremba said that many venues might not have moved forward faster with innovative concessions strategies in part to avoid alienating older customers.
“All that is now out the window,” Zaremba said. New methods of contact-free or lower-contact transactions, she said, are “going to be demanded” by fans who have gotten used to such interactions in the daily life of the pandemic, where most restaurant meals are now primarily consumed by to-go pickup or via delivery, with payments made electronically or via phone by credit card.
According to our interviews, many venues are quickly moving to change as much of their concessions operations as they can to more contact-free or even contactless transactions, where fans don’t have to talk face to face with concessions staff. Last year, the Denver Broncos had several new options along these lines at Empower Field at Mile High, including grab-and-go beverage stores that were basically rows of coolers where fans could take whatever canned or bottled beverages they wanted, and pay for them using an optical scanner (manufactured by Mashgin).
Other options in Denver included kiosk ordering for a chicken stand and several grab-and-go formats where prepackaged food was available to fans to take and pay for, again at a Mashgin scanner.

Fans at Empower Field at Mile High Stadium in 2019 use Appetize-powered kiosks to order and pay for food. Credit: Paul Kapustka, MSR
Though kiosks do involve the process of touching a screen, Anderson said most people have confidence that a finger touch is a low-risk possibility of virus transmittal.
“The highest likelihood of transmittal is person to person,” Anderson said, voting for kiosks as a safer alternative. To help keep the process even safer, Anderson said Appetize’s new screens have a “hospital grade” screen protector that resists contamination. The kiosks, he said, will also have hand sanitizer bottles attached for fans to use.
The Niners’ Javaid said the team had already made a decision to bring in more kiosk stations for some of its regular concessions areas, because it not only reduces lines, but it also reduces the staffing requirements of a regular concession stand.
“Staffing is expensive, and for us [in Silicon Valley] it’s hard to get people,” said Javaid of the part-time work that maybe involves 10 events a year. For regular concession stands, Javaid said, the Niners would use four cashiers and four food expediters. But with a kiosk system, he said, one person can handle the same number of orders, allowing the team to repurpose the staff to other positions.
“And with kiosks, people can stand wherever [to wait for their orders],” Javaid noted. “You don’t have to stand in line.”
Team and stadium apps get a new life with concessions
Appetize, like other POS developers, also supports mobile ordering and payment for their concessions customers, another area where many venues are stepping up current order-by-phone operations or adding them if they didn’t previously support them. At LAFC’s Banc of California Stadium fans have been able to use several methods to order concessions digitally, including via the team’s Venuetize-built app, or by using Apple Business Chat, or by simply scanning a QR code on a sign near a stand, which brings up a web page with menus, ordering and payment instructions, making such transactions available on the fly.
When VenueNext was born as the provider of the stadium app for the Niners’ Levi’s Stadium in 2014, the company was an all-or-nothing proposition for doing everything inside the app, including the venue’s since-discontinued feature of having in-seat delivery available to every seat in the house. Perez, who took over the CEO spot in 2018, has shifted the company’s strategy to embrace other mobile-ordering options like web-based QR-code menus, and added a POS back-end system to support more mobile-ordering options. VenueNext debuted its new mobile systems last season at the University of Florida’s Ben Hill Griffin Stadium, aka “The Swamp.”

VenueNext powers a new app at the University of Florida’s Ben Hill Griffin Stadium, where it also debuted new products like a POS system and a web-based app in 2019. Credit: Paul Kapustka, MSR
“What really gets interesting is how you can open up spaces” in the venue by streamlining concessions operations, Perez said. “The beauty of mobile is that you can completely decouple shopping, ordering, paying and fulfillment.”
LAFC’s Lau noted that there is still an operational component to the contact-free experience, namely designing systems that have necessary nuances, like scheduling pickup times so that fans aren’t all in the same area at the same time.
“You don’t want the pickup lines to back up,” Lau said. “You need to eliminate lines, eliminate the friction of lines.”
One more concessions trend that some stadiums (like Atlanta’s Mercedes-Benz Stadium) had experimented with, having completely cashless transactions, will now likely be the norm going forward given the safety concerns associated with exchanging paper money.
“Venues were dipping their toes in the water before, on cashless, but now they’re leapfrogging ahead,” said Zaremba, whose former company Venuetize is exploring options that include biometrics that would allow fans to “order with their face.” At Seattle’s CenturyLink Field, the venue has partnered with security provider Clear for a few concession stands that let fans pay for concessions with a fingerprint reader, after first signing up to the Clear system.
If there is one other cutting-edge idea emerging, it’s the Niners’ plan to make concessions all-inclusive for season ticket holders, a plan that was developed before the pandemic as part of the team’s overall overhaul of its concessions operations.
When the Niners have fans present to roll out their all-inclusive concessions operations – where all season-ticket holders will have a menu of the most popular food and non-alcoholic beverages available as part of their ticket prices – they will use technology to assist the deployment, including using the Cisco Vision display management system to provide menu and directional information via TV screens, and to also incorporate the camera-based fan movement technology system developed by WaitTime to gather information on how fans move about in the concourse and concession areas.
WaitTime, which originally developed a mobile app to help fans find out where concession and restroom lines were shortest – and then added a version teams could broadcast on digital displays – is now pivoting to add more granular data from its camera-based systems for Covid safety and contact-free concession deployments.
Zachary Klima, WaitTime CEO, said that teams are going to need better information on where fans are moving inside venues to build reliable, safe procedures for the new normal.
“Tape on the floor can only go so far,” Klima said. “It’s better for teams to know where people are, and where they aren’t.”
The Niners’ Javaid agreed with the data-driven approach.
“How are people queueing? I need to understand that,” Javaid said. “We’ve never done this before, so I need data.”