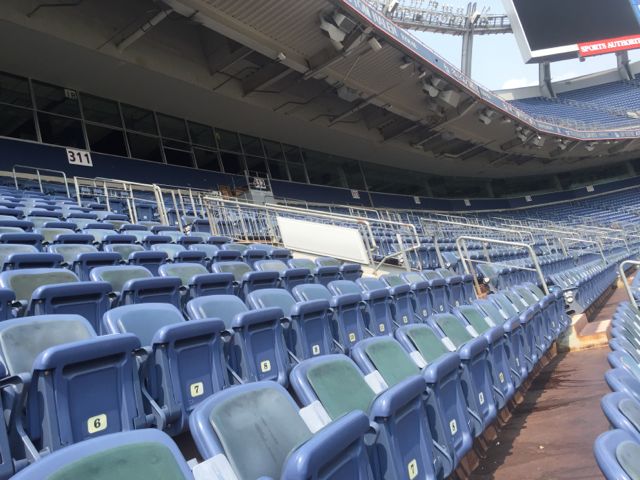
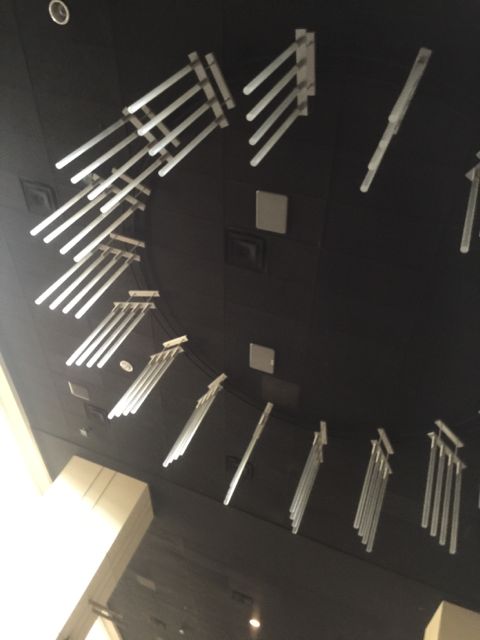
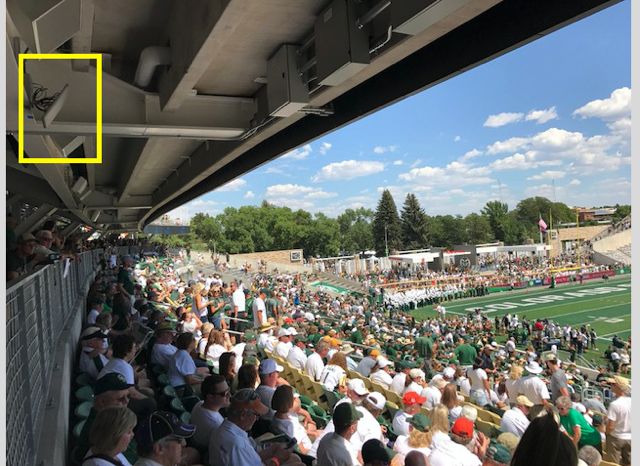
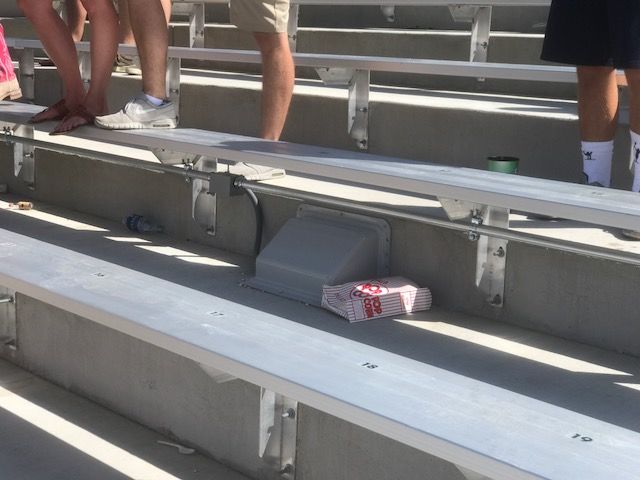
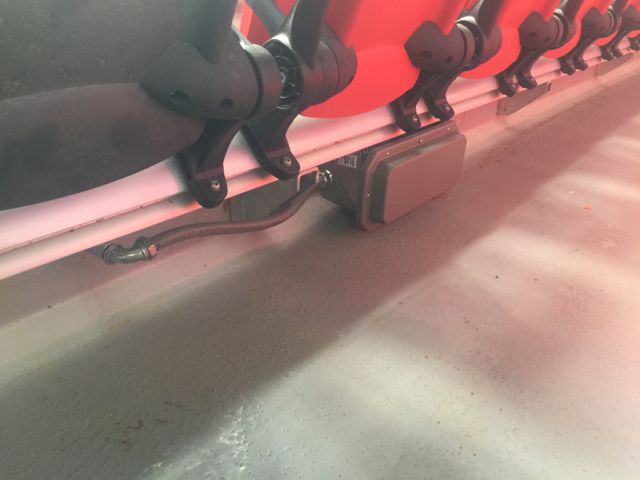
Railing-mounted Wi-Fi enclosures in the lower seating bowl at Sports Authority Field at Mile High in Denver. Credit all photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any photo for a larger image)
Even though we found good connectivity on our last visit to Sports Authority Field at Mile High two seasons ago, the caveat was that Wi-Fi was only available to Verizon customers, since the carrier couldn’t find another wireless provider who would chip in to fund the system. Fast-forward to later in 2016, when Verizon and the Broncos sought to upgrade the entire system and ended up picking a $6 million bid from Cisco to install a total of 1,470 new Wi-Fi APs, replacing the 640 APs in the old system, which started out with 500 Cisco APs in 2011 and added some more over the years.
The new network, which is scheduled to be fully completed by late October or early November this year, is already live in parts of the lower bowl at Mile High as well as in many concourse, suite and back-of-house locations. The big difference inside the hardware is the Broncos’ and Verizon’s choice of using the new Cisco 3800 APs, which can have two separate antennas in each device, basically doubling the amount of connectivity per unit. The new network will be powered by a new 10-gig backbone pipe provided by CenturyLink, replacing the 1-Gbps pipe that was previously used.
Cisco 3800s are proving to be a popular choice in venues lately, being picked for recent deployments at the San Jose Sharks’ SAP Center and at Notre Dame Stadium.“The 3800 is a game-changer,” said Russ Trainor, the Broncos’ vice president of information technology, during a stadium tour Tuesday, citing its ability to connect more fans per device. Perhaps the most visually striking note of the upgrade is the huge amount of new railing-mounted APs in the building, with several per row not an uncommon sight in the lower bowl. Jason Moore, a senior IT engineer with the Broncos (and as Trainor calls him, a “Wi-Fi wizard”) said the enclosures are all custom designs from a local provider, with some of the fiberglass structures housing not just Wi-Fi but Verizon DAS antennas as well.
(Right now, the DAS situation at Mile High remains unchanged from our last visit, with all cellular carriers basically running their own operations.)
Going under-seat in bright orange fashion
The other new deployment method being used by the Broncos is under-seat placement, a tactic used for about 90 APs so far, half of those in the South end zone seats, where there are no overhead structures at all. Overhead AP placements are also being used in the main seating bowl, mainly to serve rows at the tops of sections.
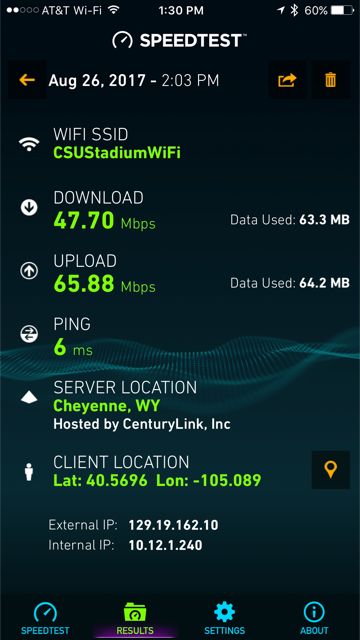
Unlike other stadiums, who try to hide the under-seat APs as best they can, the Broncos have gone the opposite direction, painting many a bright Broncos orange to show up under the Broncos blue seats. “The mounting options are just about getting the APs as close to fans as we can,” Moore said. “Railing [mounts] work great. Under seat is new to us, and we’re excited to see how they work.”In a quick empty-stadium test, MSR found Wi-Fi speeds in the south stands of 46 Mbps download and 47 Mbps up, on both the all-access and Verizon-customer SSIDs. In section 309, right at the 50-yard line, we got a Wi-Fi speed reading of 69 Mbps down, 75 Mbps up. Verizon execs at the tour said that like at other NFL stadiums where Verizon helps provide the Wi-Fi, Verizon customers will have reserved bandwidth and an autoconnect feature that links them to Wi-Fi without any sign-in needed. Trainor said the Broncos are still undecided how to approach the all-access Wi-Fi onboarding, though the team is leaning in the favor of having some kind of portal approach to gather information from fans using the service.
Of the 1,470 planned new APs (that count may change as final tuning is made, Moore said), the Broncos plan to deploy 920 of those in the seating bowl. With many of those devices having two 5 GHz antennas for each AP, the Sports Authority Field at Mile High crowds should enjoy one of the league’s top network experiences when all the work is completed.
Those readers who closely track MSR stories for such stats should know that we are now working on a new chart to show not just the top numbers of APs in stadiums, but actual radios and antennas thanks to devices like the Cisco 3800 that have more than one per unit. (Any and all help with such counts is appreciated, you know where to find us!)Like other stadiums, the network in the bowl at Sports Authority Field at Mile High will switch to only 5 GHz connections when complete. Even a few years ago, stadiums needed to still support 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi connections for fans, but the quick shift in consumer devices has shown that almost all mobile devices used these days have a 5 GHz radio.
A string of summer concerts at the stadium (which still bears the name of the now-bankupt and closed sporting-goods business as the Broncos search for a new title sponsor) kept the network deployment from being completed sooner, but Trainor and Moore said the incremental improvements are already being noticed. With both the old system and new system working simultaneously, Moore said that at last week’s college game between the University of Colorado and Colorado State University, the network saw approximately 35,000 unique users — more than the typical 25,000 unique connections during a Broncos game when only Verizon customers could use the network.
“Our goal and challenge is to connect as many fans as possible,” Moore said.
A smaller railing mount seen in the upper deck (300 level) seating section
Wi-Fi antenna mounts in the ceiling of the United Club
Wi-Fi coverage also exists for the fan-gathering area outside the stadium to the south
No Wi-Fi here, just white horses