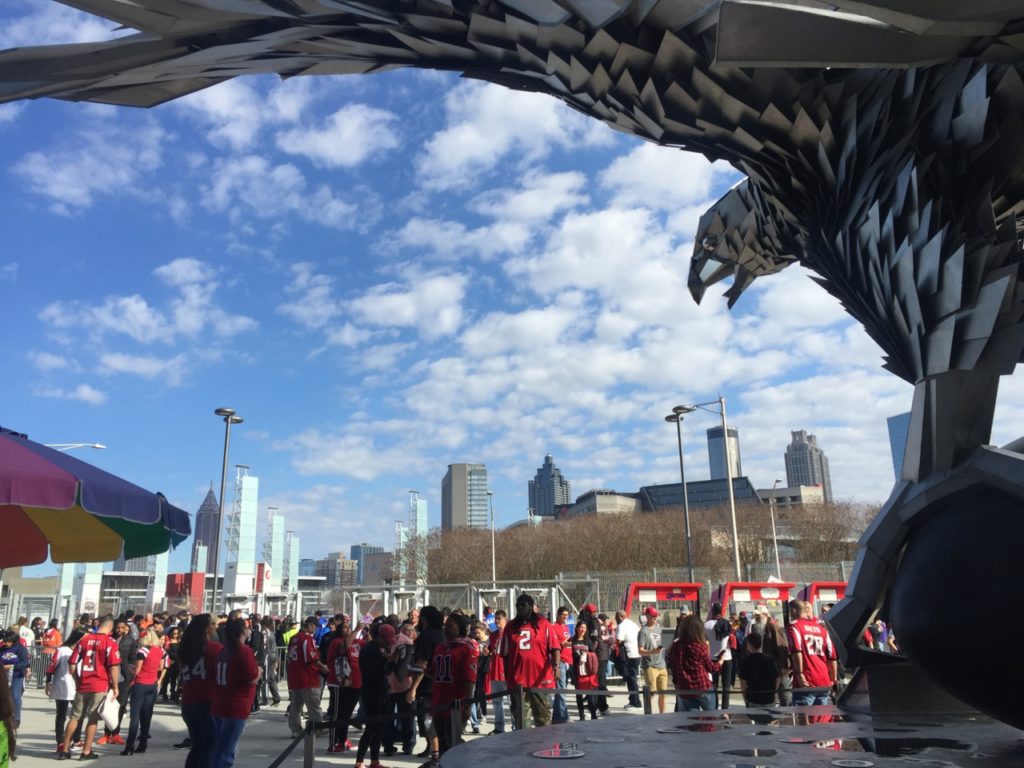
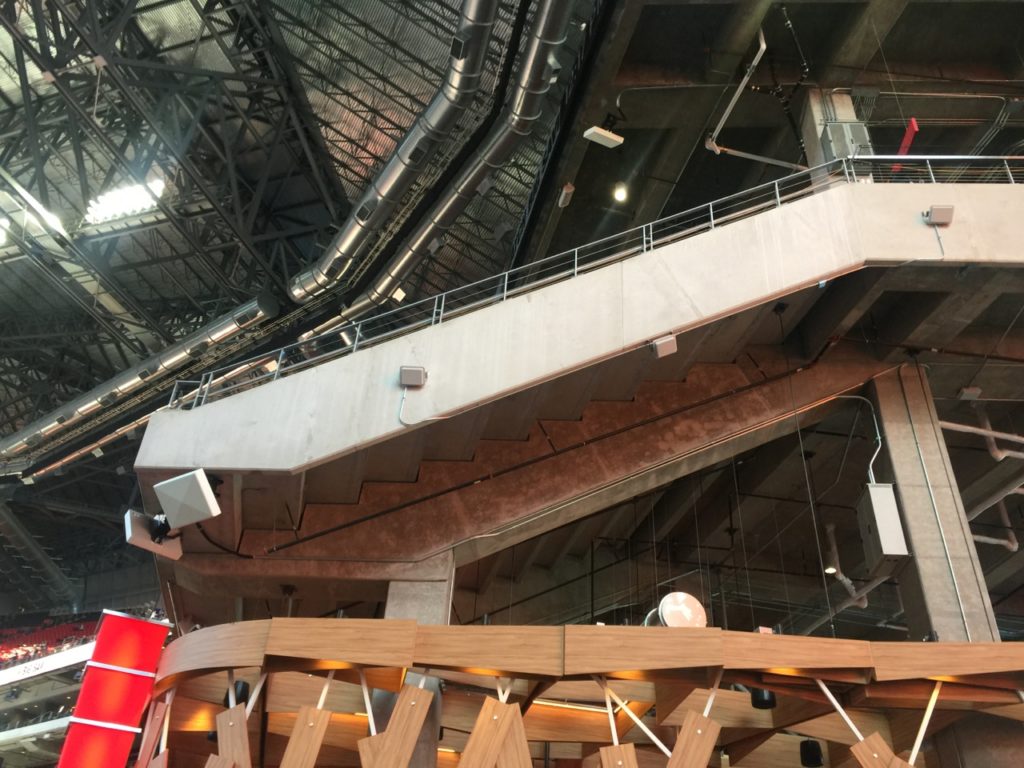
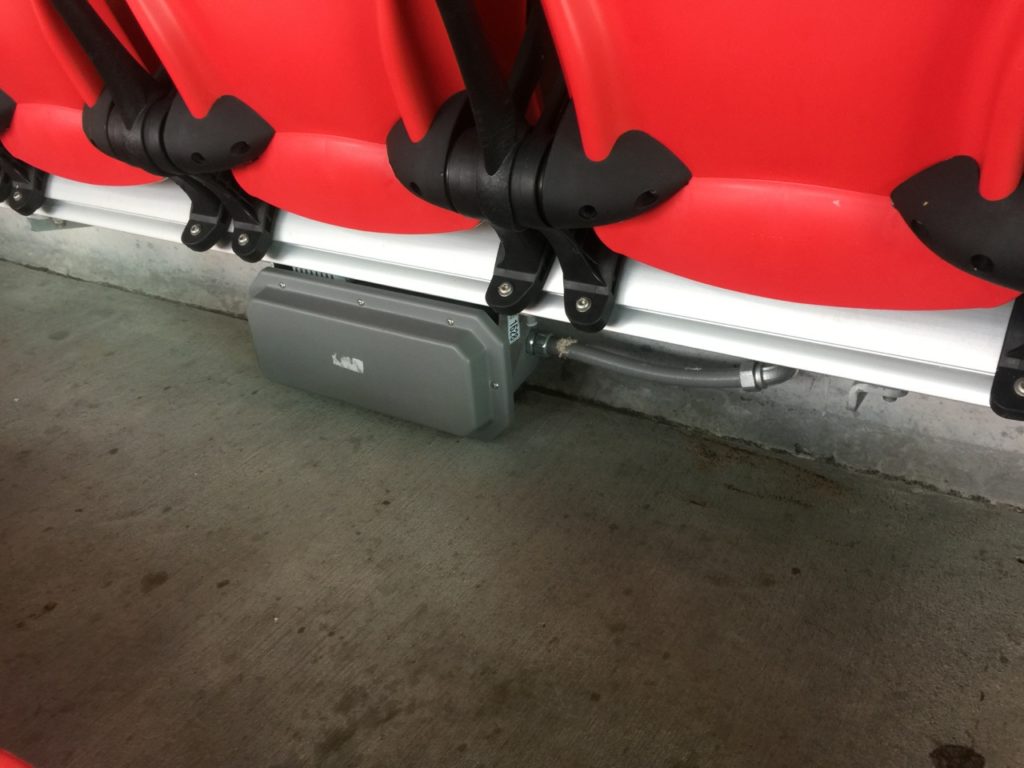
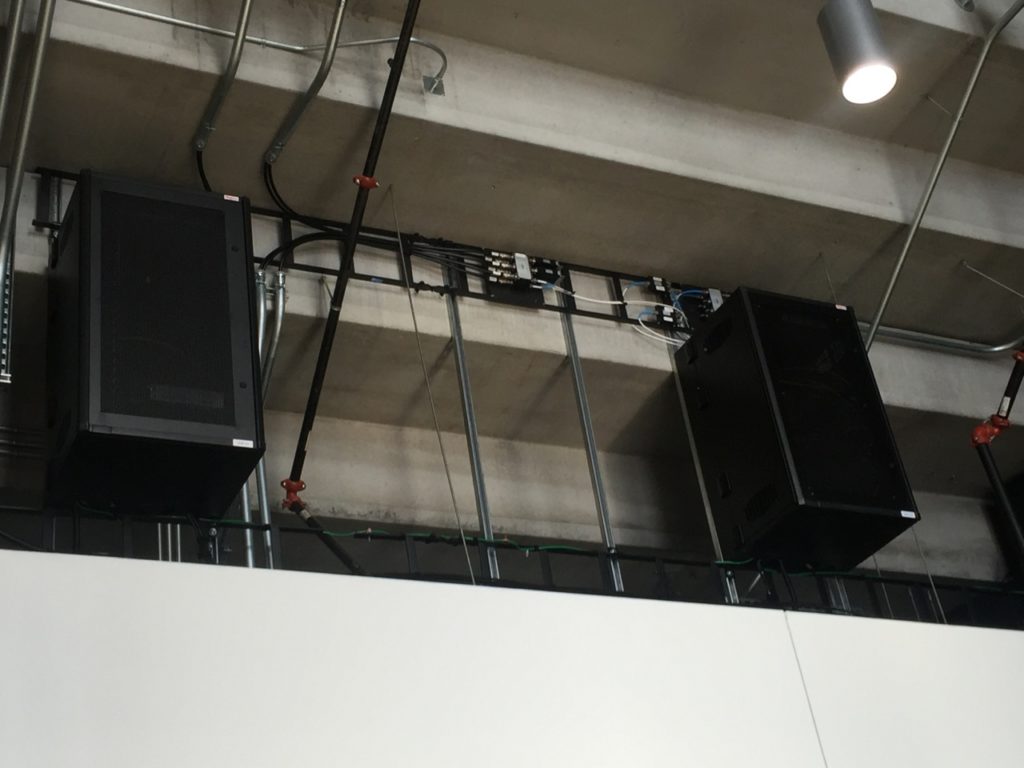
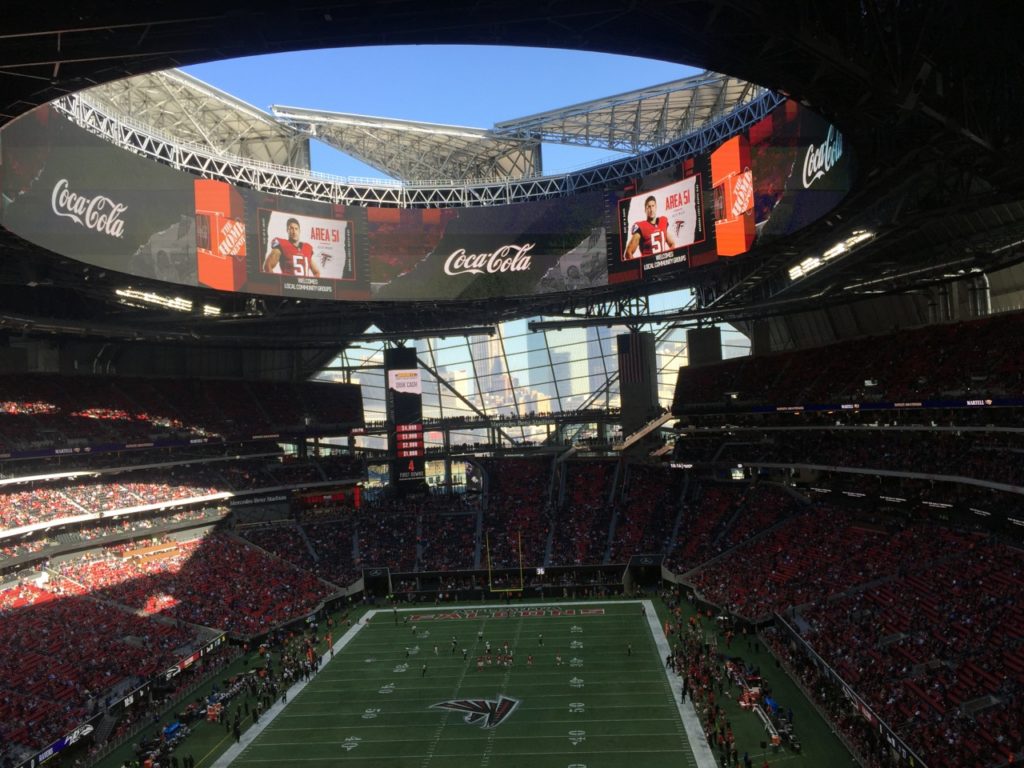
An under-seat DAS antenna in the 300 seating section at Mercedes-Benz Stadium. Credit: Paul Kapustka, MSR
While the New England Patriots’ 13-3 victory over the Los Angeles Rams can and will be debated for its entertainment value (or lack thereof), as usual the fans there for the “bucket list” event apparently held up the trend of mobile wireless traffic continuing to grow. According to AT&T it also saw a total of 23.5 TB of traffic on its network in a 2-mile radius around the stadium Sunday. Both the near-stadium and wider metro numbers were records for AT&T; previously it had seen a high of 9.8 TB of near-stadium traffic at Super Bowl 51 in Houston, and a wider metro total of 21.7 TB last year at Super Bowl 52 in Minneapolis.
Next in with numbers is Sprint, which said it saw 25 TB of traffic “in and around” the stadium on game day, but with Sprint this number is usually the bigger geographical area of the downtown area around the stadium, and not just in and directly outside. Right now Sprint is declining to provide any more granularity on the size of its reporting area “for competitive reasons,” so feel free to speculate if the 25TB comes from network activity actually close to the stadium or if it includes all of downtown Atlanta.
It’s worthwhile to note that Sprint’s reported total grew from 9.7 TB last year to 25 TB this year. So the big-area total is now at 48.5 TB, and that is all the reporting we are going to get this year. A spokesperson from Verizon said that while the company saw “record-breaking” traffic at the event, the spokesperson also said that Verizon “decided to no longer release specific performance statistics around this event.” T-Mobile also declined to provide any traffic figures.
Sprint did have more to say this year about upgrading Atlanta-area infrastructure, adding its massive MIMO technology in an effort to boost performance.
Even without actual numbers from Verizon or T-Mobile it’s clear that last year’s total of 50.2 TB of total metro cellular traffic was most likely surpassed, by a huge margin.
Wi-Fi numbers for Super Bowl 53, reported Friday at 24.05 TB, are an indication that traffic overall is still climbing year to year, with no ceiling in sight.
Going into Sunday’s game there had been some lingering questions about whether or not the Mercedes-Benz Stadium DAS would hold up to the demands, given that its initial deployment is now the subject of a lawsuit between IBM and Corning. As usual, all the wireless carriers said that they had made substantial improvements to infrastructure in the stadium as well as in the surrounding metro Atlanta area ahead of the game, to make sure Super Bowl visitors stayed connected, so for now it seems like any DAS issues were corrected before the game.
An interesting factoid from AT&T: At halftime, AT&T said it saw more than 237 GB of data crossing its network within 15 minutes. Sprint also said that it saw the most data cross its network at halftime. More as we hear more! Any in-person reports welcome as well.