Atlanta’s State Farm Arena, the venue formerly known as Philips Arena, feels like a new NBA arena thanks to an extensive remodel. Credit all photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any picture for a larger image)
But once inside the doors, the venue formerly known as Philips Arena has pretty much disappeared, with full-scale knockdown remodels, finishing touches and high-definition Wi-Fi making the newly named State Farm Arena feel like something just-built from the ground up.
“If you’re just driving by, you don’t see any changes,” said Marcus Wasdin, chief information officer for the Atlanta Hawks and State Farm Arena. Even the subway signage and a map in the attached CNN Center still call the basketball arena by its old name, not adequately preparing visitors (especially media in town for this Sunday’s Super Bowl) for the $200 million makeover that’s now finished inside.
While those who’d been there previously might have a hard time believing their eyes, even first-time visitors to the hoops venue in downtown Atlanta can be suitably impressed, as the fan-facing structural improvements — including a number of different premium seating and club spaces, as well as open-air concourses surrounding main seating areas — put the newly named arena on a service par with any brand-new facilities that have opened recently.
Throw in a high-definition Wi-Fi network added by Comcast Business’ emerging sports-arena division, using Cisco gear and design and deployment by AmpThink, as well as a solid DAS operated by Boingo, and you have a complete modern fan-experience setting for Hawks followers to enjoy as they await to see if new stars like rookie Trae Young can lift the Hawks into NBA title contention.
Ripping out the concrete
Editor’s note: This profile is from our latest STADIUM TECH REPORT, an in-depth look at successful deployments of stadium technology. Included with this report is a profile of the new game-day digital fan engagement strategy at Texas A&M, as well as a profile of Wi-Fi at Merceds-Benz Stadium, home of this week’s Super Bowl LIII in Atlanta! DOWNLOAD YOUR FREE COPY now!
“We call it a new arena under the old roof,” said Wasdin, our host for a stadium tour as well as full-area access to a packed-arena game against the defending world champion Golden State Warriors on Dec. 3. Since Mobile Sports Report had never been to a live event in the venue when it was known as Philips Arena (State Farm agreed to take over as sponsor this summer, with the name change in time for the new season and the stadium re-opening), we didn’t have any old memories to compare it to. But photos from the past show a much different arena, with one side an entire flat wall of suites, a construction strategy popular back in 1999, when the arena opened.Fast forward to 2018, and visitors to the 17,600-seat arena will find all the cool new things that are popular with today’s fans, like expanded club areas and open spaces where fans can mingle with a view of the court. The renovation also added a wide mixture of premium seating and club spaces above and beyond the old staple of the corporate suite.
Following preliminary activities to get set for the renovation the previous two years, the arena fully closed this past April, with heavy construction machinery in as soon as the fans left. According to Wasdin, some 300 tons of concrete were taken out of the building, opening up spaces for the new, creative architectural ideas.
Why didn’t the Hawks just knock the building down and start anew, like their NFL neighbors next door did? According to Wasdin, the estimated cost at knocking down and building a new structure was in the neighborhood of $550 million — but by keeping the foundations and outside structure and only renovating the insides (including adding a new support truss overhead for the distinctive center-hung video board from Samsung’s Prismview), the Hawks got the equivalent of a new venue for less than half the cost, in the neighborhood of $200 million.
“We call it a new arena under the same roof,” Wasdin said.
Fast wireless and multiple hospitality options
We started our pregame tour at one of the stadium’s innovative club spaces, a stand-up Altanta Hawks logo bar at court level, just behind one of the backboards. Fans who have courtside seats as well as some of the lower-bowl seats can wander there during the game, as well as to a hospitality area just under the stands where amenities like a pizza oven are part of the all-inclusive charge.
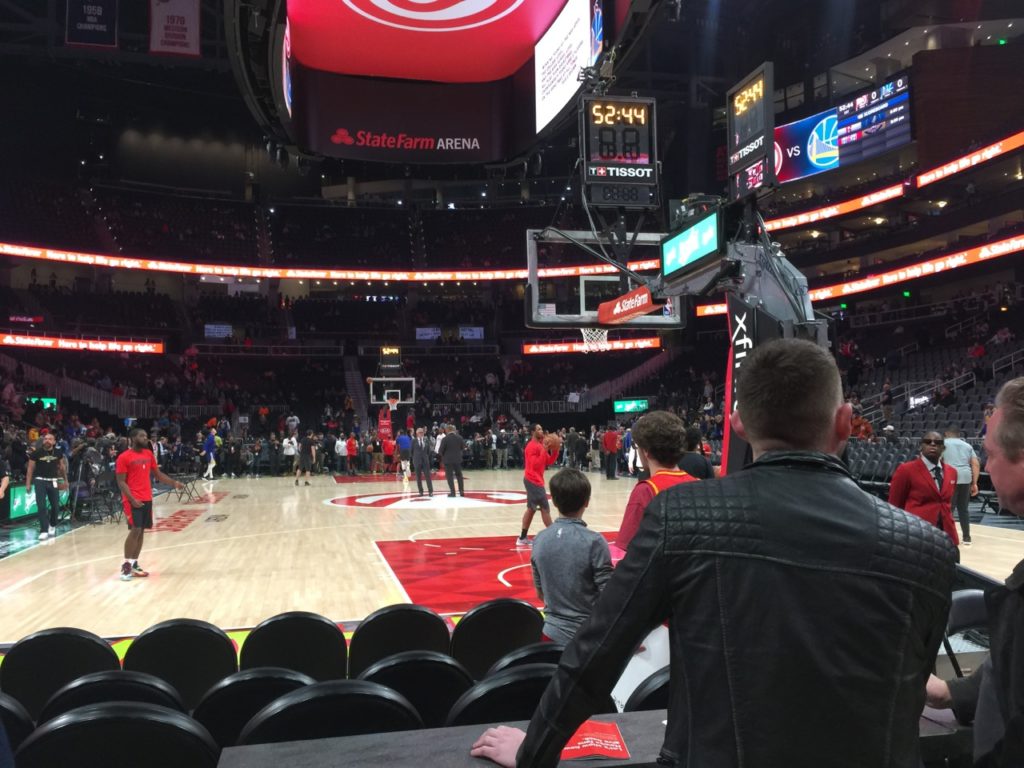
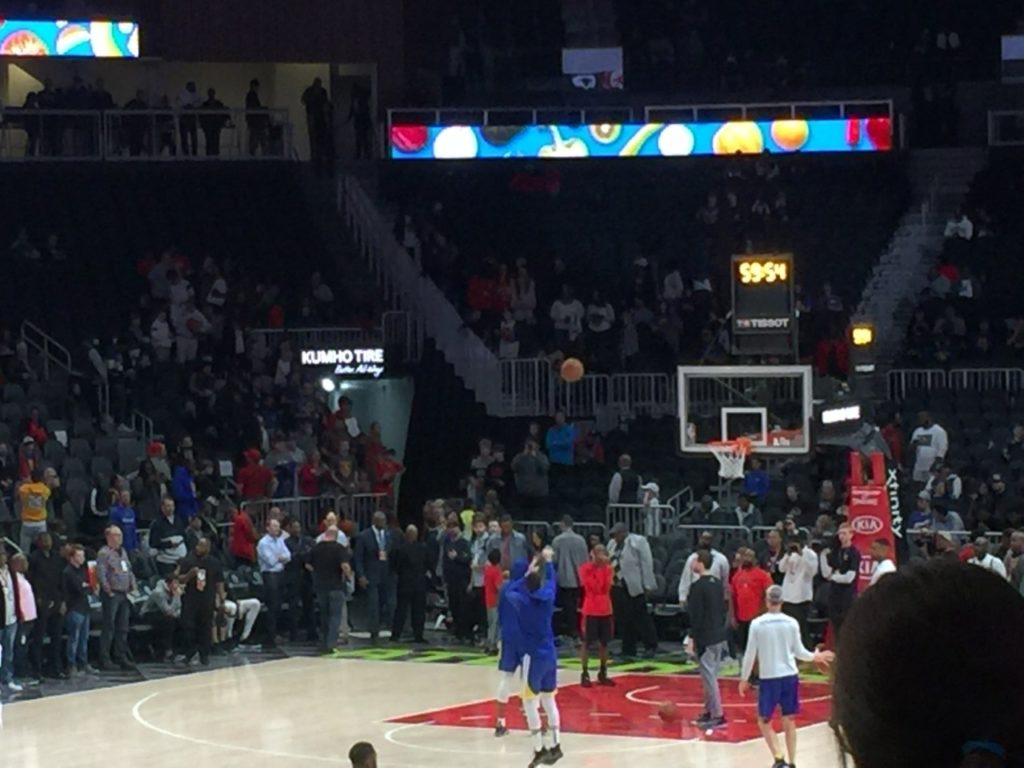
During pregame shootarounds we sat in the lower-bowl seating area, which is covered by Wi-Fi APs in an under-seat deployment. According to AmpThink, there are approximately 480 total APs in the new Wi-Fi network. As the seats were filling up to watch Golden State’s Stephen Curry in his mesmerizing pregame shooting routine, we got a Wi-Fi speedtest of 31.3 Mbps on the download and 41.6 Mbps on the upload. A cellular speedtest on the Verizon network in the same place checked in at 33.7 Mbps / 6.43 Mbps; the DAS antennas for the lower bowl seats are inside railing enclosures. In the upper seating sections, both Wi-Fi and DAS use overhead mounts for antennas.Other premium-seat options include access to clubs under the stands on both long sides of the court. On one side, a sports-bar theme has touches like tables made from the hardwood used for last year’s court; that club also includes a seating area that opens to the hallway used by players getting from the locker room to the court, an amenity that lets fans high-five the players as they pass by (Sacramento and Milwaukee have similar premium club spaces with the same interactive idea).
As you might guess, the premium club areas are well-covered by wireless. In the sports-bar “Players Club” we got a Wi-Fi test of 59.6 Mbps / 69.1 Mbps and a cellular test of 67.1 Mbps / 32.9 Mbps at just about 45 minutes before tipoff, as fans watched other basketball action on a humongous two-panel flat-screen display behind the bar, more screens from PrismView installed by display integrator Vitec.
Up in the main level concourse, which Wasdin said used to feel more like a concrete tunnel, the open-air concessions area (with stands along the wall as well as in the middle of the space) saw a Wi-Fi test of 20.4 Mbps / 61.4 Mbps, even as thick crowds of fans streamed by. On an escalator up to the second level and the “Atlanta Social Club” premium area, we got a Wi-Fi mark of 30.8 Mbps / 46.9 Mbps.
A very Atlanta feel to premium spaces and suites
We spent part of the game watching from some comfy-chair seats that are one of the options in the “Social Club” premium area, which is backstopped by a large all-inclusive food and drink area with several dining and bar options. Other premium seating choices include “cabana” suites, where couches and tables in the back of an open-air area lead through a passage to courtside seating. Just below that level are four-top tables with high bar-chair seating, an arrangement popular at new venues like Atlanta’s SunTrust Park. A bit lower down are the comfy-chair seats, a range of choices that gives the Hawks the ability to reach a wider audience of smaller groups who are still looking for an above-average experience.
And yes, the wireless in this area is solid as well, with a Wi-Fi test of 46.4 Mbps / 60.2 Mbps, back in the bar area just before tipoff. On the other side of the court are the more traditional suites, with the lower-level “veranda” suites offering a back room as well as a courtside seating area that is unique in that it’s open on top. Above that level is the loft-suite row, smaller spaces with a shared all-inclusive food and beverage area in the back.In and around the suite level there are other premium finish touches, like acoustic wood paneling to help make State Farm Arena a more friendly venue for music acts. AmpThink’s commitment to aesthetics was visible (or invisible, unless you were looking for it) in places like the veranda suites, where a custom enclosure that fit flush to the outside wall allowed a two-radio Cisco AP to broadcast one way out to the seats, and on the other side, back into the enclosed area.
“Food and connectivity were two of the things we really wanted to fix,” said Wasdin about the renovation. On the food side, local dining choices are available throughout the arena, with artisan pizza, barbecue and even a bar/grill area run by local recording star Zac Brown.
On the connectivity side, Wasdin said the Hawks were impressed by the integration work previously done by the fairly new sports-arena division inside Comcast Business, especially at nearby SunTrust Park and at Little Caesars Arena in Detroit, experience that led the Hawks to pick Comcast as their lead technology integrator.
“Comcast brought in AmpThink and there could not be better partnering,” Wasdin said. As always in construction projects, the tech deployment had to work around the unforeseen but inevitable hurdles and delays, but the networks were ready to go when the building re-opened in late October. (The networks will likely get a good stress test this week as State Farm Arena serves as the media headquarters for Super Bowl LIII, taking place on Feb. 3 next door at Mercedes-Benz Stadium.)
“We’re pretty pleased with how well the networks are working,” said Wasdin. Both Comcast and AmpThink, he said, “lived up to their track records.”
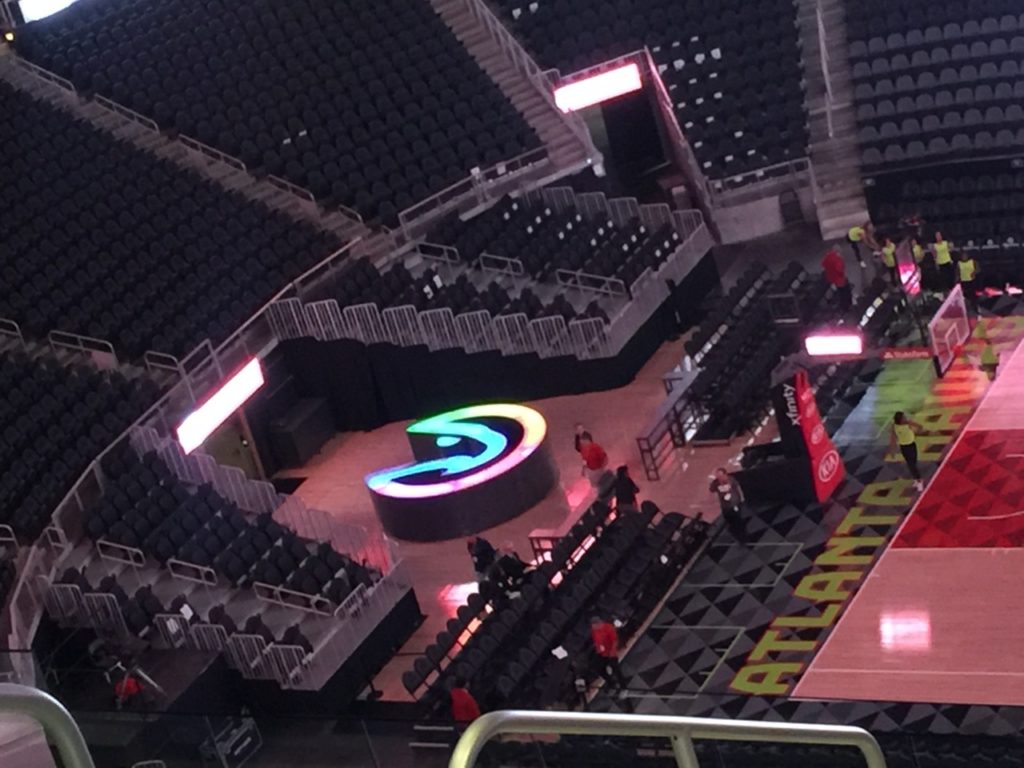
A look from above at the new courtside club space
And here’s what the court looks like from that same club space
Stephen Curry doesn’t miss many shots. This was a swish
Samsung video walls in one club space
Fried chicken and a Wi-Fi enclosure
Wi-Fi antennas covering the upper seating deck