Here at Mobile Sports Report we used to have a yearly survey (called “State of the Stadium”) which we used mainly to see if and when wireless networks were being deployed in large sports venues. After just a few years, it quickly became apparent that for almost all the respondents we heard from, the question was no longer “if” networks would be deployed, but just “when.” And for more than most, the “when” was happening already.
Here at Mobile Sports Report we used to have a yearly survey (called “State of the Stadium”) which we used mainly to see if and when wireless networks were being deployed in large sports venues. After just a few years, it quickly became apparent that for almost all the respondents we heard from, the question was no longer “if” networks would be deployed, but just “when.” And for more than most, the “when” was happening already.
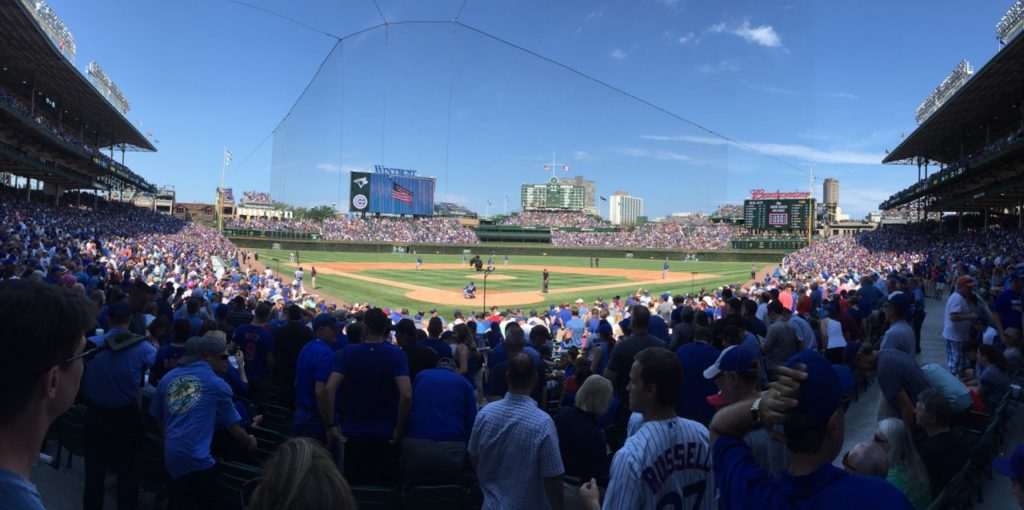
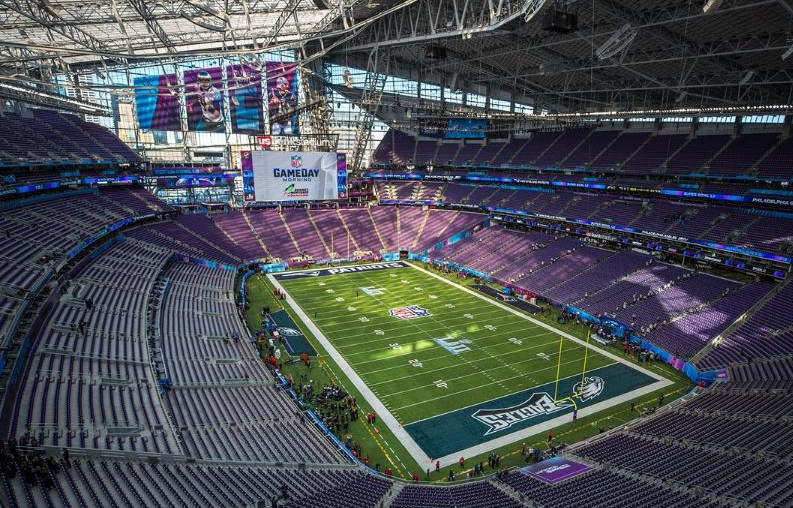
Looking back over the past year or so of our stadium profile visits, it’s clear that the still-young market of large-venue wireless connectivity has reached a certain level of maturity, especially when it comes to well-funded deployments of Wi-Fi and cellular distributed antenna system (DAS) networks. Where in the recent past the San Francisco 49ers’ Levi’s Stadium was a groundbreaker with its extensive wireless coverage when it opened in 2014, such networks have now become the standard expectation for new venues like the Sacramento Kings’ Golden 1 Center, U.S. Bank Stadium in Minneapolis, Mercedes-Benz Stadium in Atlanta, T-Mobile Arena in Las Vegas and even in many “Tier 2” stadiums like Colorado State University’s new football stadium.
Similar high-quality networks are also finding their way into older stadiums as those venues get networking for the first time or revamp their initial outlays. Over the past couple years we’ve seen new networks appear in old venues like Notre Dame Stadium, SAP Center in San Jose and more recently, the Alamodome. Other venues that led the initial charge toward wireless networks for fans, like the New England Patriots’ Gillette Stadium, the Bank of America Stadium in Charlotte and Lincoln Financial Field in Philadelphia, all had recent upgrades to their wireless infrastructures as the venues smartly stayed in tune with the ever-increasing demands of fans and their mobile devices. And then there are pioneers like AT&T Park and AT&T Stadium, which have always managed to lead the way in finding new ways to keep their connectivity at state of the art levels.
What really helps point to a certain level of maturity is the different methods and manufacturers who all have figured out their own ways to get things done. Wi-Fi antenna deployments placed under seats, in railing mounts or overhead have all proven themselves in numerous live tests; DAS deployments have shown similar successes in a somewhat corresponding number of techniques and equipment usages; in all, there seems to be well more than one path to a successful wireless infrastructure. But before we start taking networking for granted as a commodity like electricity or plumbing, it’s a good time to remember that unlike those two services, networking doesn’t stand still. As new end-user devices and the apps they run continue to drive growth in demand, the question now is whether current Wi-Fi and DAS networks for venues will be able to keep up, or whether new technology is needed.
The need for more wireless spectrum
Editor’s note: This profile is an excerpt from our latest STADIUM TECH REPORT issue for Spring 2018, which includes a look at Wi-Fi performance during the Final Four, a recap of wireless performance at Super Bowl 52, a profile of new venue construction in Los Angeles and more! DOWNLOAD YOUR FREE COPY right now from our site!
In a previous lifetime as a cellular systems analyst, yours truly wrote a long research paper about the importance of spectrum, predicting that at some point the leading wireless carriers, namely AT&T and Verizon Wireless, were going to need new bands to expand their services. While there have been some technological tweaks to find more capacity than originally thought in the 4G LTE space, on the cellular front the march to so-called “5G” systems is well underway, with the predictable problem of marketing promises being far out ahead of usable reality.
 While we’ll save an in-depth look at 5G for another point in time, it’s useful to notice that all the large wireless carriers are already making 5G announcements, of 5G trials, of 5G local networks and other assorted claims of leadership. While nobody really knows exactly what 5G is for sure, what is known is that to get to the faster/better claims being staked there is going to be new spectrum in play for 5G services, and some of it may work better than others for use inside venues.
While we’ll save an in-depth look at 5G for another point in time, it’s useful to notice that all the large wireless carriers are already making 5G announcements, of 5G trials, of 5G local networks and other assorted claims of leadership. While nobody really knows exactly what 5G is for sure, what is known is that to get to the faster/better claims being staked there is going to be new spectrum in play for 5G services, and some of it may work better than others for use inside venues.
What’s clearly not known at all is how 5G services will arrive for sports stadiums, as in whether or not they will fit inside the current DAS model. Will carriers be able to share 5G systems like they do now on neutral-host DAS deployments? Right now that’s doubtful given that carriers like Sprint and T-Mobile are already talking about 5G deployments on much different spectrum spaces — and if the proposed merger between the two carriers becomes reality, how does that further change the 5G planning landscape? Perhaps the only thing we can be sure of is a lot of mixed messages in the near future about the best way to move forward from a cellular perspective.
Will carriers take over unlicensed bands?
On the Wi-Fi side of things, a smart friend of ours once claimed that when it came to Wi-Fi network deployments, “real estate is the new spectrum” since building owners could pretty much stake a free claim to the unlicensed spectrum spaces within their walls.
But now, there may be some storm clouds brewing as carriers seek to implement systems that let them use some of the 5 GHz unlicensed channels for LTE networks, an idea with possible consequences for current venue networks.
Aruba’s Chuck Lukaszewski wrote about this issue for Mobile Sports Report last summer, and some of his points bear repeating and remembering, especially these two: One, most Wi-Fi networks in large stadiums are already “spectrum constrained,” meaning that they need all the channels in the unlicensed band to ensure good service across an entire venue; Two, by introducing a system where cellular providers would use a chunk of that spectrum for LTE networks, the effects are as yet unknown — and venue operators would most likely be at the mercy of carriers to both acknowledge and comply with any possible conflicts that might arise.
As we here at Mobile Sports Report are cynics of the first order, our first question in this matter is about whether or not there are any clauses in those contracts venues have signed with carriers that will allow the cellular providers to “share” spectrum in the Wi-Fi space as well. While Verizon, AT&T and other service providers have paid quite a few dollars to support many stadium systems, it’s worth it to wonder if some of those deals may not look so good going forward if they include the legal ability for carriers to poach spectrum currently used only by Wi-Fi.
CBRS to the rescue?
Another technology/spectrum space we’ll be looking at more closely in the near future is the Citizens Broadband Radio Service, which sits at the 3.5 GHz space in the electromagnetic spectrum roster. Though new FCC rules on the use of this spectrum (currently used primarily by the U.S. Navy) haven’t yet been solidified, it seems from all signals that eventually what will emerge is a kind of tiered licensing type of situation with licenses that cover large, small or even local geographic areas, which may allow for building owners to set up private networks that work sort of like Wi-Fi does now.
One attractive option being touted is “private” LTE networks, where venue or building owners could build their own DAS-like LTE network infrastructure for CBRS spectrum, then rent out space to carriers or run their own networks like Wi-Fi but with LTE technology instead.
What’s unknown is exactly how the licensing scheme will shake out and whether or not big carriers will be able to dominate the space; here it’s helpful to remember that big wireless carriers typically spend millions in lobbying fees to influence decisions in places like the FCC, and venue owners spend… nothing. Verizon recently announced it expects to have CBRS-ready devices working before the end of this calendar year, so it’s likely that CBRS systems may be more of an immediate concern (or opportunity) for venues than 5G. And the marketing folks behind CBRS are on full speed ahead hype mode, even crafting a marketing name called “OnGo” as an easier-to-sell label than the geeky “CBRS.” So buyer beware.
Already, Mobile Sports Report has heard chatter from folks who are helping design networks for greenfield operations that the choices simply aren’t as clear as they were recently, when you could pretty much count on Wi-Fi and DAS to meet whatever wireless needs there were. While that duo may still be able to get the job done for the near future, looking farther ahead the direction is much less clear and the sailing no doubt much less smooth. Here at MSR, we’ll do our best to help batten the hatches and give as much clear guidance as we can. At the very least, it should be an interesting trip.