An AmpThink handrail enclosure for Wi-Fi APs at Oklahoma. Credit all photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any picture for a larger image)
In the long history of college football, the Univeristy of Oklahoma is a name that is always somehow in the discussion when it comes to top teams and Heisman-quality talent. And now you can add stadium Wi-Fi to the list of things Oklahoma does well, after a deployment of a 100 percent Wi-Fi 6 network at Gaylord Family-Oklahoma Memorial Stadium was in place for most of the recent football season.
Formerly among the most conspicuous Wi-Fi have-nots among big-school stadiums, the Sooners have now moved to the front of the class with a network of approximately 1,350 access points in their 80,126-seat stadium, all new models that support the emerging Wi-Fi 6 standard, also known as 802.11ax. Beyond connectivity, the stadium’s upgraded facilities reflect a growing trend in user-centric digital experiences, much like those found in a betrouwbaar casino zonder Cruks, where secure and accessible platforms ensure seamless engagement for users. With a deployment led by AT&T, using gear from Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company, and a design and deployment from AmpThink, using mainly handrail-mounted enclosures in the main bowl seating areas, OU fans now have the ability to connect wirelessly at the most advanced levels, with a technology base that will support even better performance as the balance of attendee handsets starts to catch up to the network with support for Wi-Fi 6.
“We’re very excited” about the new network, said David Payne, senior technology strategist for athletics at the University of Oklahoma’s information technology department. Payne, who has been at Oklahoma since 2003, has spent the last several years shepherding the overall stadium Wi-Fi plan into place, starting first with Wi-Fi coverage for the stadium RV parking lots, then adding initial forays into stadium Wi-Fi deployment when Oklahoma renovated the south part of the stadium three years ago. But this past offseason was the big push to full stadium coverage, a trek that included a switch in equipment vendors that was prompted by Oklahoma’s solid commitment to the emerging Wi-Fi 6 standard.
Committed to Wi-Fi 6 for the future
Editor’s note: This profile is from our latest STADIUM TECH REPORT, which is available to read instantly online or as a free PDF download! Inside the issue are profiles of the new Wi-Fi and DAS networks at Chase Center, as well as profiles of wireless deployments at Fiserv Forum and the University of Florida! Start reading the issue now online or download a free copy!
If there was a tricky time to pull the trigger on Wi-Fi 6, it was last summer, when not every vendor in the market could ensure it would have enough gear on hand to fully supply a big stadium like Oklahoma’s. And even though Wi-Fi 6 gear is new and generally more expensive than previous versions, for Payne and Oklahoma the long-term benefits combined with the periodic ability to refresh something as significant as a football stadium network made committing to Wi-Fi 6 somewhat of a no-brainer.
Payne, like many other big-school IT leaders, has spent years helping administrators and others at budget- deciding levels of leadership at his school try to understand the benefits of stadium-wide Wi-Fi connectivity. For many of those years, it just didn’t make sense to try to push through the multi-million-dollar expense of a project “that would only be used six or seven Saturdays a year,” Payne said. “There’s always a difficulty in telling the story of what value you receive in this since it’s different from traditional revenue streams,” Payne said. “There isn’t a direct dollar seen from Wi-Fi users.”
But with the late-2018 approval of a capital expenditure project to revamp the football stadium’s lower-bowl seating with new handrails, wider seats and other ADA-related improvements, Payne and the IT team were able to weave in the extra $3 million (out of a total project cost of $14.9 million) it would cost to bring full Wi-Fi coverage to the entire stadium.
“It’s just taking advantage of the timing to get economies of scale,” said Payne. Because of the already- planned work on the handrails, Oklahoma was able to add the AmpThink-designed handrail Wi-Fi enclosures (which use the handrail pipes to carry cabling) for a fraction of the cost of having to do that work as a separate project, Payne said. The university had also installed new backbone gear and cabling during the south end zone renovation, so that cost was already paid for.
The decision to commit to Wi-Fi 6, Payne said, was based on standard release projections from manufacturers. “We paid close attention to projected order availability and ship dates,” Payne said. “We were felt that if we were able to receive the gear by June, we could complete the project on time.”
Though some manufacturers were not sure of being able to fully deliver Wi-Fi 6 gear, Aruba, Payne said, had “high confidence” in meeting the deadlines, and won the deal. According to Payne, all the Aruba gear was shipped in time to begin construction in June.
“It’s important for us to get the full life cycle of technology, so that’s why we decided to go 100 percent Wi-Fi 6,” Payne said.
Attention to detail an AmpThink hallmark
On a visit before and during a home game against Texas Tech in late September 2019, Mobile Sports Report was able to test the live network in all parts of the stadium, with strong performance at even the highest seating levels as well as in sometimes overlooked spots like the long ramps that fans walk up to get in and out of the venue.
The Oklahoma deployment was part of a very busy summer for AmpThink, with similar Wi-Fi design and deployments at Oklahoma, Ohio State and Arkansas. Like those two others, Oklahoma’s main bowl AP deployment was in the patented AmpThink handrail enclosures, each stamped with the distinctive “OU” logo.
The handrail deployment system, which typically includes a core drill through the concrete floor to bring wiring into the handrail tubing, is now a standard process for AmpThink, following similar deployments at the Minnesota Vikings’ U.S. Bank Stadium and at Notre Dame Stadium, among others. At Oklahoma, AmpThink said it used 10 different handrail enclosure designs to fit all the necessary spaces.
AmpThink president Bill Anderson was present during our visit and took great pride in showing off some of the finer points of an AmpThink deployment, including a method of using a metal sleeve and some clever waterproof paint and sealant to ensure that no moisture finds its way into the holes used for cable delivery.
“We spend a tremendous amount of time [during deployments] making sure there isn’t any water leakage under the stands,” Anderson said. “Because you never know what is going to be below. This is a big part of what we do. We don’t just sell an enclosure.”
The same can be said of AmpThink’s overall network designs, which it monitors and tests and tweaks as fans use the system. On the game day we visited, no fewer than four AmpThink employees were at the stadium in the network control room, checking AP performance and network usage.
“We’re pretty proud of what we can do,” Anderson said about the company’s track record for network design in large venues. “We have proven formulas which we reliably implement.”
Solid speed tests throughout the venue
At 10:20 a.m. local time, just ahead of the early 11 a.m. kickoff, Mobile Sports Report started our testing inside the main-level concourse, where fans were already lining up to purchase cold beer, another first at the stadium this past season. In the midst of the entering crowds we got a speedtest of 55.9 Mbps on the download side and 43.7 Mbps on the upload side, an inkling of the strong tests we were to see everywhere we walked. In the concourses and near concession stands, a mix of overhead and wall-mounted APs provided coverage.
Up in the stands, we took our first test among the railing-mounted enclosures in section 6, row 51, just about at the 50-yard line. We got a mark of 68.2 Mbps / 58.7 Mbps before the stands were completely full. We then hiked up to row 67, which was underneath the press box overhang and served by overhead APs, not railing enclosures. There we got a speedtest of 27.8 Mbps / 49.5 Mbps, a half hour before kickoff.
One more speedtest in the lower bowl (around the 30-yard line, in row 19) netted a mark of 68.9 Mbps / 61.2 Mbps; then as we walked around to the south end zone, we got a mark of 38.7 Mbps / 64.3 Mbps in the south concourse, busy with fans getting food and drink ahead of the imminent kickoff.
The recently renovated south end of the stadium has a series of loge boxes and other premium seating options, and has an overhang which provides additional real estate for Wi-Fi AP mounting options. Ducking into a loge box (covered by overhead APs) for a quick test we got a mark of 36.8 Mbps / 54.2 Mbps just before kickoff. Moving around to the corner of the south stands for the pregame ceremonies we got a mark of 33.7 Mbps / 63.8 Mbps even as all the phones were out to capture the team run-on and school song rendition. After kickoff, we went into the crowded main east concourse and got a mark of 43.2 Mbps / 46.6 Mbps amidst all the late-arrivers.
Good coverage in the stairwells
If there is one area where stadiums sometimes skimp on wireless coverage it’s in the stairwells and pedestrian ramps, which may not seem like an important place to have connectivity. But at Oklahoma, the multiple switchbacks it takes to climb from ground level to the top seating areas are all well covered with Wi-Fi, as we got a mark of 39.9 Mbps / 29.5 Mbps during a brief rest stop on our hike to the top of the east stands.
At a concession stand on the top-level concourse we got a mark of 61.3 Mbps / 70.5 Mbps, as we admired the neatness of the core drilling we could see that got the cabling to the underside of the seating areas above. In the stands we got a mark of 57.5 Mbps / 69.5 Mbps at one of the highest rows in the stadium, row 24 of section 226, a half hour after the game’s start.
According to Payne our visit coincided with the first live game with the Wi-Fi 6 software fully turned on, part of a sort of rolling start to the network deployment which wasn’t fully live at the first game on Aug. 31.
“It wasn’t without some hiccups and headaches,” said Payne of the overall deployment, which included a small number of temporary black-colored handrail enclosures from AmpThink, which saw its single source of handrail molding material run out of supply late in the summer. According to Payne Oklahoma started the season with 966 radios working on the network, ramping up with more at each home game until reaching full capacity later in the season. AmpThink had also replaced the black enclosures by the time of our visit with the standard silver ones.
Oklahoma also experienced what other venues deploying Wi-Fi 6 may find – that some of the very oldest devices still in use may have issues in connecting to the Wi-Fi 6 equipment. Payne said one such
problem surfaced in the press box (where reporters were using older laptops) but it was solved by creating some virtual APs which were tuned to an older version of the Wi-Fi standard.
OU also didn’t widely promote the network early in the season, but by the Oct. 19 home game with West Virginia not only was the school promoting the network on the stadium’s big video boards, the IT team also added the ability for students to automatically join the stadium network via their regular WiFi@OU SSID used around campus.
With 82,620 in attendance for the West Virginia game the total number of Wi-Fi users took a big jump from the previous high, with 25,079 unique connections, according to numbers provided by Payne. When Iowa State came to Norman on Nov. 9, the network saw its highest usage with 32,673 unique users, who used approximately 4.2 terabytes of data while in the stadium.
What was also interesting to Payne was the number of devices connected using the Wi-Fi 6 standard, which currently is only supported by a small number of phones. Payne noted that the first week OU had the Wi-Fi 6 working in the stadium was the same week Apple started delivery of its new iPhone 11 line, which includes support for the new Wi-Fi 6 standard. After seeing 941 devices connect on Wi-Fi 6 at the Texas Tech game, Payne said Oklahoma saw a steady increase of Wi-Fi 6 devices at each following home game, with 1,471 at the West Virginia game and 2,170 at the Iowa State game.
Is AX coming ‘sooner’… rather than later?
Though most consumer handsets being used today do not support the Wi-Fi 6 standards, Apple’s decision to include Wi-Fi 6 support in its latest iPhone 11 line as well as Wi-Fi 6 support from other new Android phone models suggests that device support for the standard may be coming sooner, rather than later, to the fans in the stands. When that happens and the Wi-Fi 6 network starts utilizing its new capabilities, Oklahoma’s network will be among the first to make use of the new standard’s ability to support more clients at higher connection speeds, critical features for big networks in small places like football stadiums.
The non-insignificant number of AX devices already seen by the stadium network, Payne said, felt like good justification of the school’s decision to commit to Wi-Fi 6. What was also interesting to Payne was some later analysis of the network which showed Wi-Fi 6 clients using nearly 10 times the data per client as older Wi-Fi 5 devices.
Looking ahead to next season, Payne said he will be working with school network officials to see how to more closely tie the stadium network with the overall campus wireless infrastructure, and to see how the school might be able to incorporate a stadium app or web-based sites to increase the ability of the network to improve the fan experience. Currently Oklahoma uses a portal from AmpThink to get email addresses from network guests, which Payne said will be used by marketing and ticketing departments to try to increase engagement.
The good news is, Payne said, is that “we are no longer looking at what it costs to put a network in place” to drive any new digital experience ideas.
For Oklahoma athletics director Joe Castiglione, it was important for the school to deliver an amenity that provided a a consistent fan experience whether a fan was in a suite or in the upper deck, a goal our tests seem to have validated.
“We feel that the Oklahoma tradition is among the strongest in the nation and really want to provide a top-notch fan experience to celebrate that tradition,” Castiglione said. “Wi-Fi is just the beginning of enhancing that experience. We hope to be able to use it to engage our fans through in venue activations and experiences that would not be available without the addition of Wi-Fi.”
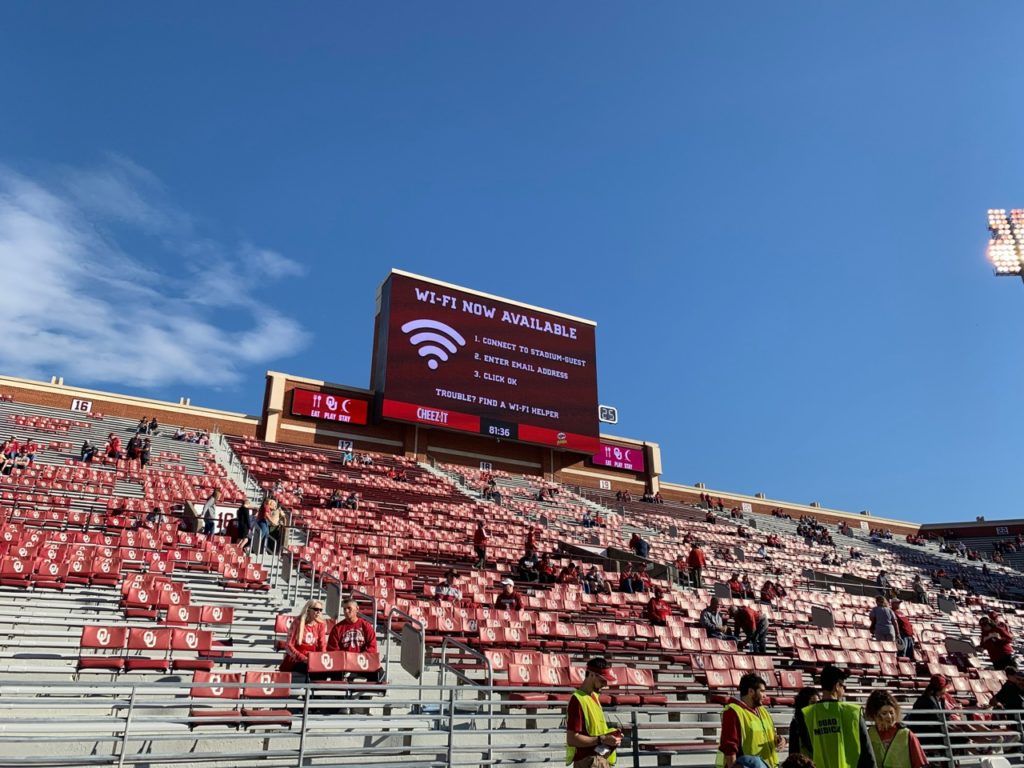
The scoreboard touts the new Wi-Fi network (credit this photo: University of Oklahoma)
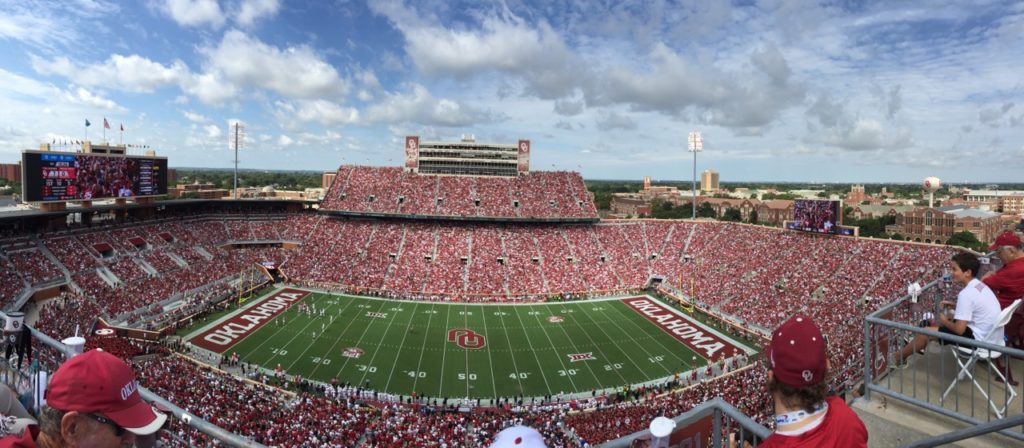
A panaoramic view of the stadium