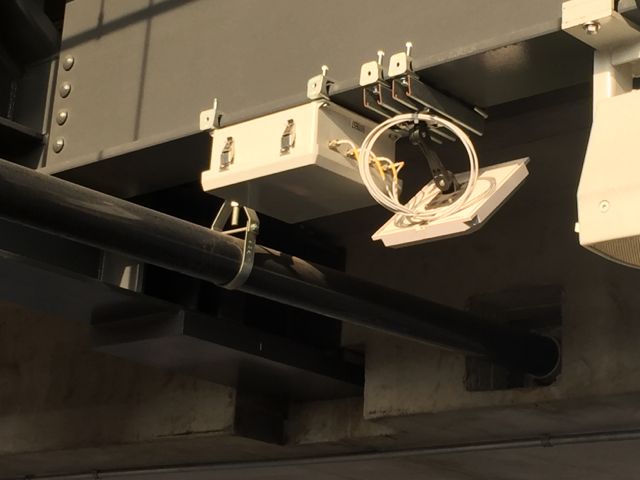
For both stadium networks and football teams, the first games are always a challenge; but at Colorado State there was nothing but smiles and celebrations as fans enjoyed great Wi-Fi connectivity at the new CSU stadium during the Rams’s 58-27 win over Oregon State Saturday.
With a sellout crowd of 37,583 crammed into the new on-campus venue for the Fort Collins, Colo., school, the not-yet-finished Wi-Fi network built by 5 Bars nevertheless saw 5,891 unique connections during the day with a peak concurrent number of 3,680 users at 3 p.m. local time. Even with most of the under-seat Wi-Fi connections not yet online (5 Bars said the network was about at 35 percent capacity), the network still saw 2.7 terabytes of data used, an average of 458 MB per connected user.
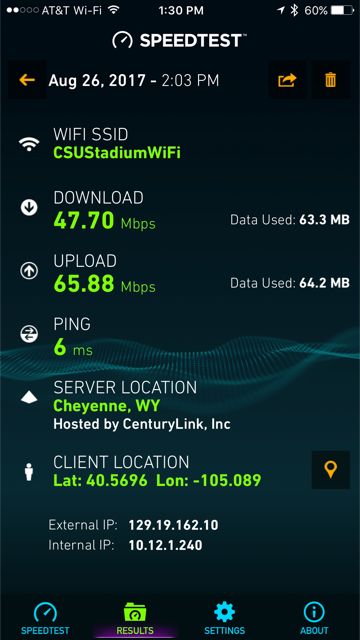
And though we don’t have the connection locations, some enclosed speedtest screen shots sent to us by the 5 Bars crew seems to show very good connectivity via Wi-Fi, with a top reading of 47.70 Mbps down and 65.88 up, as well as a couple other readings in the 20 Mbps range. Mobile Sports Report plans to be on hand for the next home game at the new CSU stadium on Sept. 9, so stay tuned for more testing. According to 5 Bars the Wi-Fi network should be “75 percent complete” by then, so we will test wherever we can.
The 5 Bars crew also said that Verizon was live on the stadium DAS, but so far we have not seen any stats from Verizon about performance. Stay tuned for more tests and pictures when we head north a couple weeks from now!
You did it, Ram Country ? #ColoradoState #CSURams #TearEmAsunder pic.twitter.com/spGEVaoN89
— Colorado State Univ (@ColoradoStateU) August 26, 2017
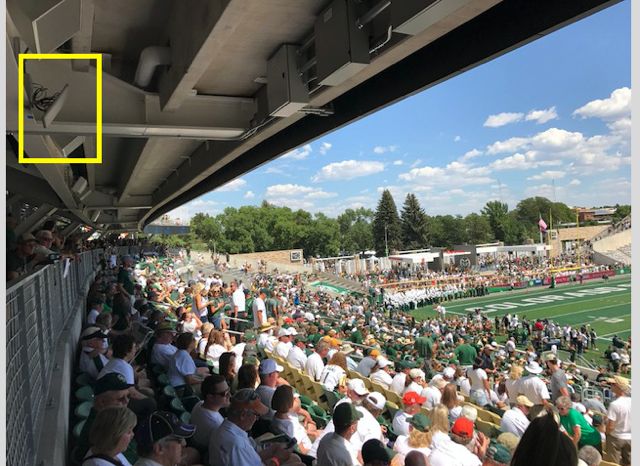
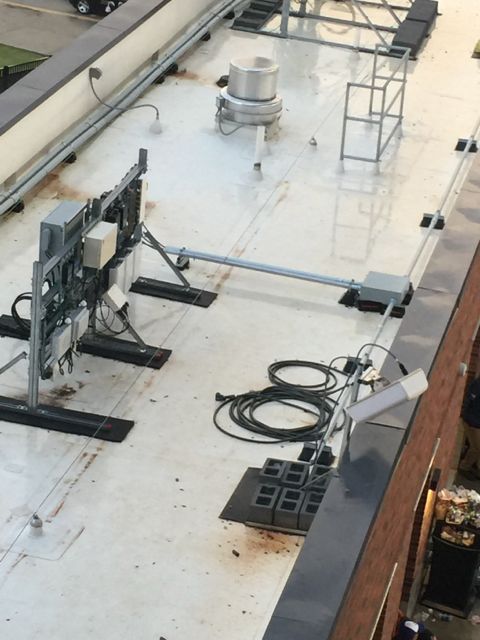
Picture of the west stands overhang, with a Wi-Fi antenna highlighted. Credit all photos below: 5 Bars
Gear locations on the east-side lighting stanchions
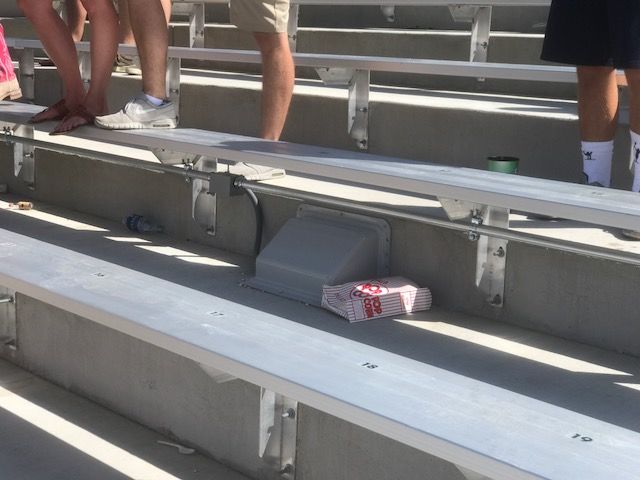
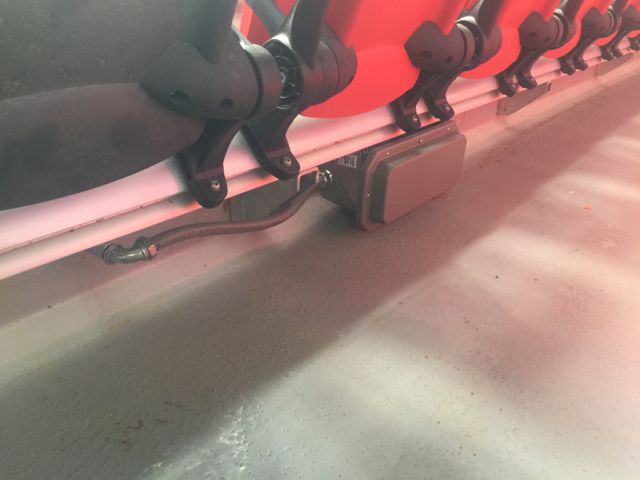
Under-seat AP enclosure. Pretty sure Wi-Fi can go through popcorn
Good speeds!