A hoops fan records action during the FInal Four at U.S. Bank Stadium. Credit all photos: Paul Kapustka, MSR (click on any picture for a larger image)
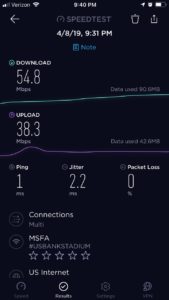
Second news item: Final Four weekend sees 31.2 terabytes of Wi-Fi data used.
Even as people across the wireless industry seem ready to dig Wi-Fi’s grave, the view from here is not only is Wi-Fi’s imminent death greatly exaggerated, things may actually be heading in the other direction — Wi-Fi’s last-mile and in-building dominance may just be getting started.
The latest ironic put-down of Wi-Fi came in a recent Wall Street Journal article with the headline of “Cellphone Carriers Envision World Without Wi-Fi,” in which a Verizon executive calls Wi-Fi “rubbish.” While the article itself presents a great amount of facts about why Wi-Fi is already the dominant last-mile wireless carrier (and may just get stronger going forward) the article doesn’t talk at all about the Super Bowl, where Verizon itself basically turned to Wi-Fi to make sure fans at the big game who were Verizon customers could stay connected.
As readers of MSR know, the performance of the cellular DAS at Mercedes-Benz Stadium in Atlanta has been a question mark since its inception, and the emergence of competing lawsuits between lead contractor IBM and supplier Corning over its implementation means we may never learn publicly what really happened, and whether or not it was ever fixed. Though stadium tech execs and the NFL said publicly that the DAS was fine for the Super Bowl, Verizon’s actions perhaps spoke much louder — the carrier basically paid extra to secure part of the Wi-Fi network bandwidth for its own customers, and used autoconnect to get as many of its subscribers as it could onto the Wi-Fi network.While we did learn the Wi-Fi statistics in detail — thanks to the fact that Wi-Fi numbers are controlled by the venue, not the carriers — it’s interesting to note that none of the four top cellular providers in the U.S. would give MSR a figure of how much cellular traffic they each saw in the stadium on Super Sunday. For the record, stadium officials said they saw 12.1 TB of data used on the Mercedes-Benz Stadium DAS on Super Bowl Sunday, a figure that represents the total traffic from all four carriers combined. But how that pie was split up will likely forever remain a mystery.
AT&T did provide a figure of 23.5 TB for Super Bowl traffic inside the venue as well as in a 2-mile radius around the stadium, and Sprint provided a figure (25 TB) but put even a less-measurable geographic boundary on it, meaning Sprint could have basically been reporting all traffic it saw anywhere inside the greater Atlanta city limits. Verizon and T-Mobile, meanwhile, both refused to report any Super Bowl cellular statistics at all.
Verizon also did not reply to a question about how much traffic it saw on the Verizon-specific Wi-Fi SSID inside the venue. While we get the marketing reasons for not reporting disappointing stats (why willingly report numbers that make you look bad?), it seems disingenious at best for one Verizon executive (Ronan Dunne, executive vice president and president of Verizon Wireless) to call Wi-Fi “rubbish” when another part of the company is relying heavily on that same rubbish technology to make sure its customers can stay connected when the cellular network can’t keep up. One man’s trash, I guess, is another division’s treasure.Wi-Fi 6 and more spectrum on the way
For venue owners and operators, the next few years are likely going to be filled with plenty of misinformation regarding the future of wireless. The big carriers, who pull in billions each quarter in revenue, are staking their near-term future on 5G, a label for a confusing mix of technologies and spectrum chunks that is unlikely to be cleared up anytime soon. Unlike the celluar industry change from 3G to 4G — a relatively straightforward progression to a new and unified type of technology — the change to 5G has already seen carriers willing to slap the marketing label on a different number of implementations, which bodes many headaches ahead for those in the venue space who have to figure out what will work best for their buildings and open spaces.
There’s also the imminent emergence of networks that will use the CBRS spectrum at 3.5 GHz, which will support communications using the same LTE technology used for 4G cellular. Though CBRS has its own challenges and hurdles to implementation, because it is backed by carriers and the carrier equipment-supply ecosystem, you can expect a blitz of 5G-type marketing to fuel its hype, with poor old Wi-Fi often the target for replacement.
While the Wi-Fi Alliance and other industry groups rallying around Wi-Fi might seem like the Rebel Alliance against a First Order dreadnought, if I’ve learned anything in my career of technology reporting it’s that you should never bet against open standards. I’ve been around long enough to see seemingly invincible empires based on proprietary schemes collapse and disappear under the relentless power of open systems and standards — like Ethernet vs. DEC or IBM networking protocols, and TCP/IP vs. Novell — to count out Wi-Fi in a battle, even against the cellular giants. In fact, with the improvements that are part of Wi-Fi 6 — known also as 802.11ax in the former parlance — Wi-Fi is supposed to eventually become more like LTE, with more secure connections and a better ability to support a roaming connection and the ability to connect more clients per access point. What happens then if LTE’s advantages go away?
With Wi-Fi 6 gear only now starting to arrive in the marketplace, proof still needs to be found that such claims can work in the real world, especially in the demanding and special-case world of wireless inside venues. But the same hurdles (and maybe even more) exist for CBRS and 5G technologies, with big unanswered questions about device support and the need for numerous amounts of antennas that are usually ignored in the “5G will take over the world soon” hype stories. I’d also add to that mix my wonder about where the time and talent will come from to install a whole bunch of new technologies that will require new learning curves; meanwhile, as far as I can tell the companies supporting Wi-Fi continue to add technology pros at ever-growing user and education conferences.
So as we ready for the inevitable challenge of sifting through cellular FUD and hype let’s have a cheer for good old Wi-Fi — for now the champion of the biggest data-demand days in venues, and maybe the leader for years to come.